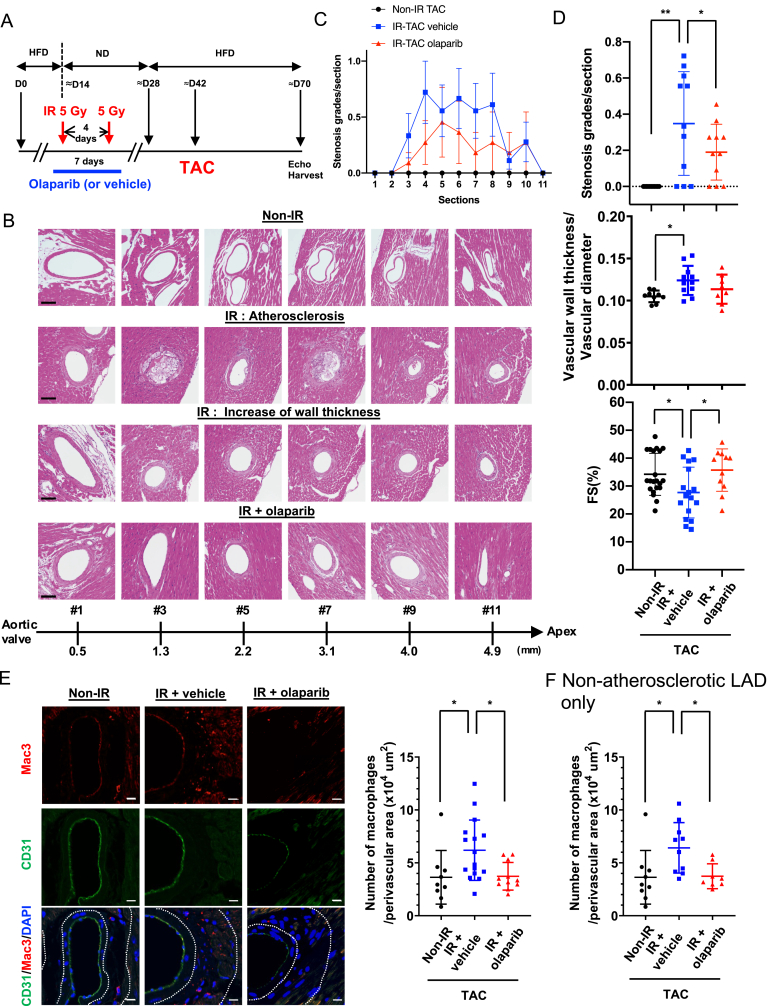
Fig. 8.
Role of PARP activation in coronary atherosclerosis, vascular wall thickening, macrophage infiltration, as well as subsequent cardiac dysfunction and myocardial infarction.(A) A schematic showing the timing of each procedure for evaluating IR-induced cardiovascular pathologies. LDLR−/- mice were fed an HFD for ≈2 weeks and exposed to localized IR (5 Gy) in the neck and thoracic area twice. Mice were fed a normal chow diet (ND) for ≈2 weeks until their body weight had recovered, as we described previously [100], and HFD feeding was restarted for ≈2 weeks. Thoracic aorta coarctation (TAC) was then performed and ≈4 weeks later, we performed echocardiography and euthanized the mice for sample collection. (B) Representative images of the left anterior descending artery (LAD) stained with hematoxylin and eosin 4 weeks after TAC at different distances from the aortic valve (AV) to the tip of the heart (Apex), depicting varying degrees of atherosclerosis and vessel wall thickness between the IR and non-IR groups. (C) Stenosis grades, as described in Methods, at different distances from AV (section #1 [AV] to #11 [apex]). Mean ± SD, (n = 11). (D) Quantification of stenosis grades (top, 11 sections examined for each group), the normalized and averaged ratio of vascular wall thickness to the vessel diameter of LAD (middle, Non-IR, n = 9 (3 male (M)/6 female (F); IR + vehicle, n = 11 (3 M/8F); IR + olaparib, n = 11 (5 M/6F)) and fractional shortening (FS) (bottom, Non-IR, n = 21 (4 M/17F); IR + vehicle, n = 17 (6 M/11F); IR + Olaparib, n = 11 (5 M/6F)) 4 weeks after TAC-surgery as indicated in A. Mean ± SD (Top) Repeated measures 1-way ANOVA, Turkey's multiple comparison test with individual variances (grades/section) were used for each comparison. (Middle and bottom) ordinary 1-way ANOVA. (E) Representative immunofluorescence staining of the coronary artery for ECs (CD31 [green]), macrophages (Mac3 [red]), and nuclei (DAPI [blue]). The number of anti-Mac3 positive cells in the perivascular region were normalized by the area of perivascular region (x10 [4] μm [2]). Mean ± SD; non-IR, n = 9 (3 M/6F); IR + vehicle, n = 16 (7 M/9F); IR + olaparib, n = 11 (5 M/6F). The area between two dotted lines is the perivascular region. Statistical significance was assessed by 1-way ANOVA and multiple comparisons were made by Bonferroni's t-test. Scale bar = 10 μm. (F) The numbers of anti-Mac3 positive cells in the perivascular region of LAD without atherosclerotic plaques were normalized by the area of perivascular region (x10 [4] μm [2]). Mean ± SD; non-IR, n = 9 (3 M/6F); IR + vehicle, n = 10 (3 M/7F); IR + olaparib, n = 8 (2 M/6F). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Macrophage infiltration into perivascular area was significantly increased by IR + TAC, which was completely inhibited by transient olaparib treatment. *P < 0.05, **.. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)