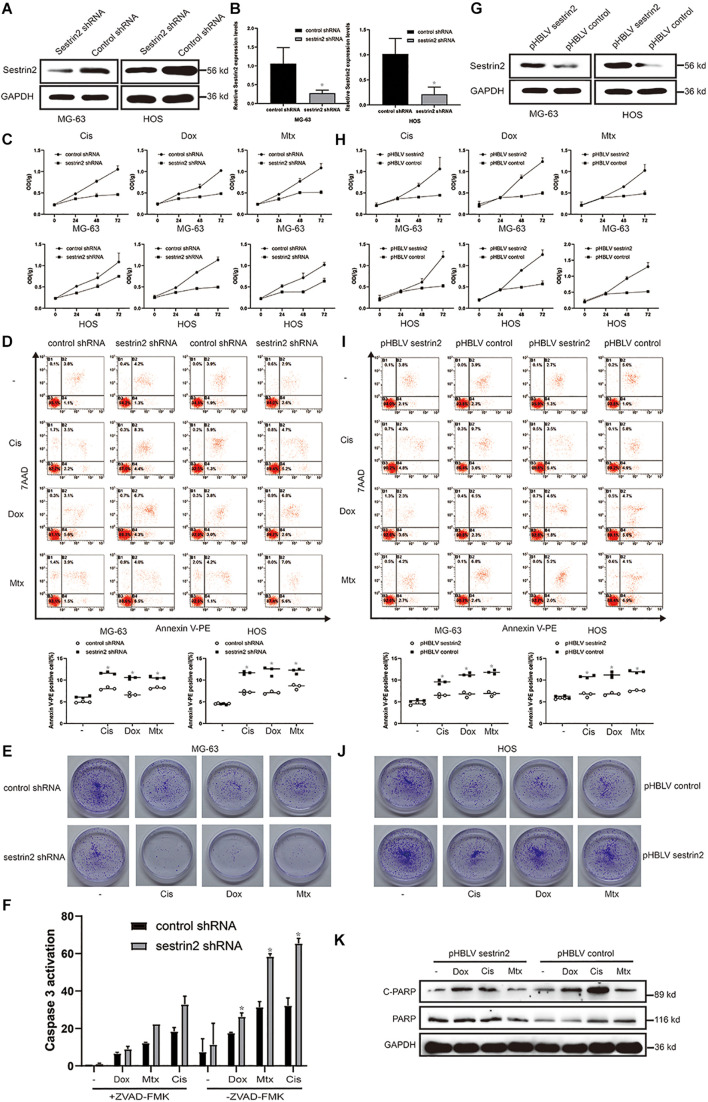
FIGURE 2.
SESN2 confers drug resistance to target cells by reducing their sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents. MG-63 and HOS cells were transfected with control shRNA or SESN2 shRNA, and the knockdown effect was detected by western blot (n = 3) and quantitative real-time PCR (n = 3) (A,B). MG-63 and HOS cells with SESN2 knockdown were treated with Cis (20 μmol/L), Dox (0.2 μg/mL), or Mtx (50 μmol/L) for 24, 48, and 72 h. Cell activity was detected by CCK-8 (C) (n = 3). After treatment for 24 h, apoptotic cells were detected by flow cytometry (D) (n = 3). SESN2 knockdown significantly reduced the number of colony-forming MG-63 cells (E) (n = 3). After MG-63 cells were treated with Cis (20 μmol/L), Dox (0.2 μg/mL) or Mtx (50 μmol/L) for 24 h, the apoptosis of cells transfected with control shRNA or SESN2 shRNA and cultured in the presence or absence of ZVAD-FMK (20 μmol/L) was detected using the Caspase 3 kit (F) (n = 3). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 vs. the Control shRNA group. The expression of SESN2 after transfection of a plasmid carrying the SESN2 gene was evaluated by western blot (G) (n = 3). MG-63 and HOS cells overexpressing SESN2 as well as their corredsponding control cells were treated with Cis (20 μmol/L), Dox (0.2 μg/mL), or Mtx (50 μmol/L). Cell viability and apoptosis were detected by CCK-8 (H) (n = 3) and flow cytometry (I) (n = 3), respectively. SESN2 increases the number of colony-forming units of HOS cells (J) (n = 3). Cleaved and total PARP in SESN2-overexpressing and control HOS cells were analysed by western blot (K) (n = 3). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 vs. the pHBLV control group.