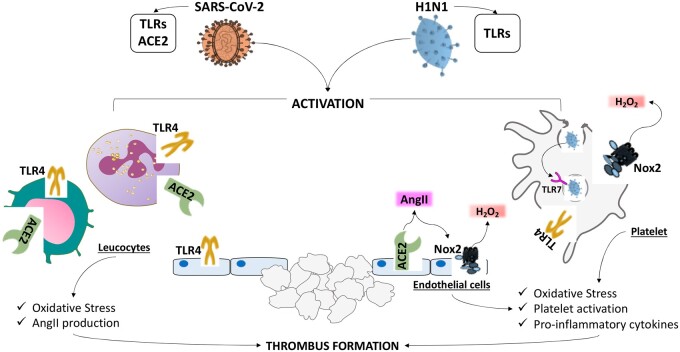
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of thrombosis in COVID-19 and CAP patients. SARS-CoV-2 and H1N1 by Toll-like receptors (TLRs) activate cells implicated in the thrombotic process such as leucocytes, platelets and endothelial cells. Upon binding to TLRs up-regulation of Nox2, the most important cellular producer of reactive oxidant species (ROS), resulting in hydrogen peroxide generation, may occur. In the case of COVID19 patients, the virus entry into the cells may occur also by its binding to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) with ensuing loss of function and angiotensin II (AngII)/Nox2 up-regulation.