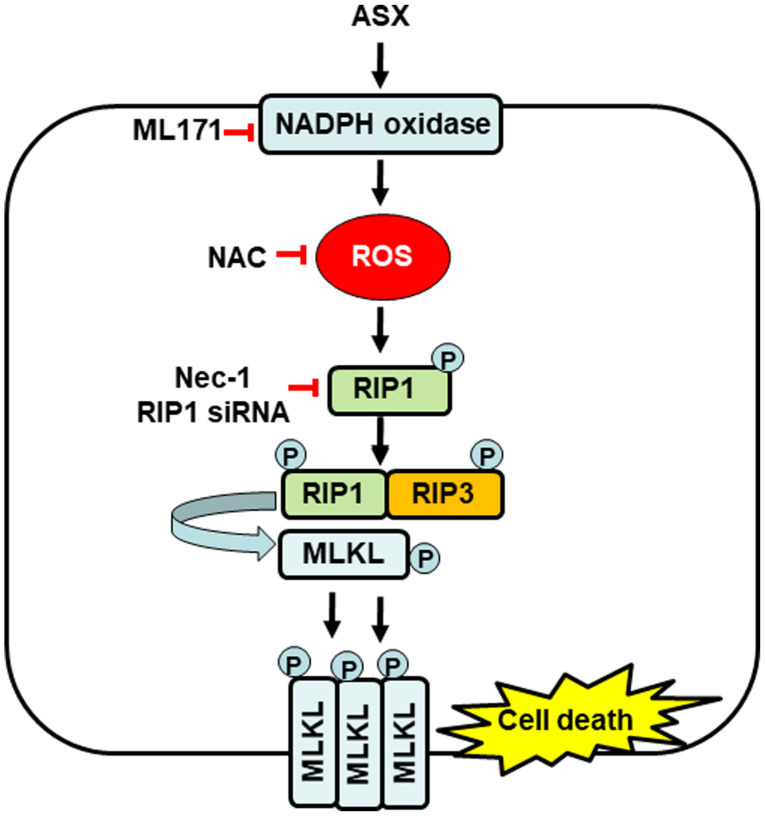
Figure 5.
Proposed mechanism by which ASX induces necroptosis in gastric cancer AGS cells. High levels of ASX (20 µM) may activate NADPH oxidase and increase the production of ROS, which induce the phosphorylation of RIP1, thus, activating RIP3 and MLKL. Activated MLKL is translocated to the plasma membrane, where it possibly ruptures the cell membrane and causes necroptosis. Treatment with NADPH oxidase inhibitor ML171, antioxidant NAC and Nec-1, a specific inhibitor of RIP1, suppresses ASX-induced necroptosis in gastric cancer AGS cells. ASX, astaxanthin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RIP, receptor-interacting protein kinase; MLKL, mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein; p-, phosphorylated; NAC, N-acetyl cysteine; Nec-1, Necrostatin-1; siRNA, small interfering RNA.