Fig. 4. Cryo-EM reconstructions of Fab-S complexes.
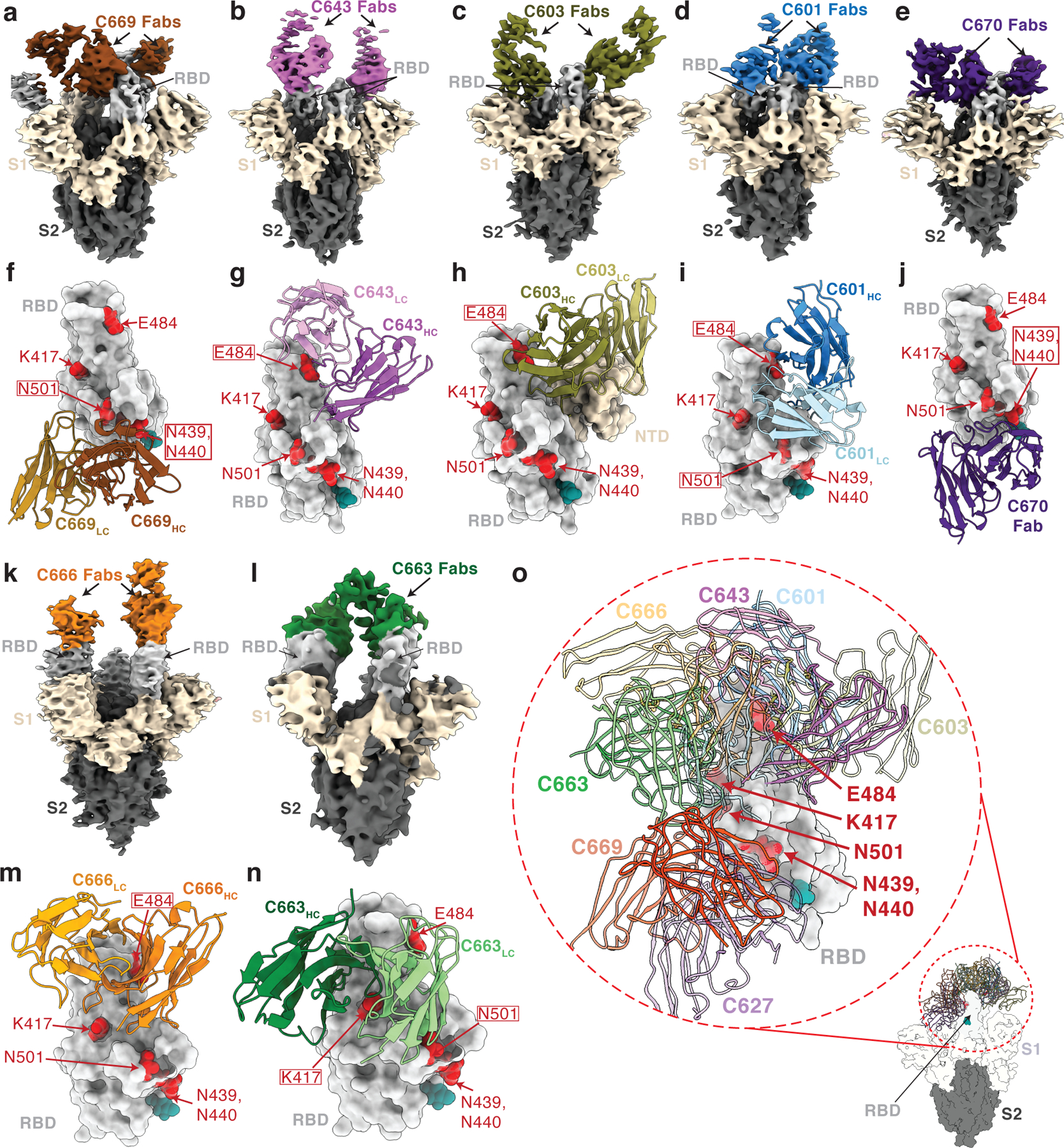
Cryo-EM densities for Fab-S complexes (a–e; k–l) and close-up views of antibody footprints on RBDs (f–j; m–n) are shown for neutralizing mAbs. As expected, due to Fab inter-domain flexibility, cryo-EM densities (a–e; k–l) were weak for the Fab CH-CL domains. Models of antibody footprints on RBDs (f–j; m–n) are presented as Fab VH–VL domains (cartoon) complexed with the RBD (surface). To generate models, coordinates of stabilized S trimer (PDB 6XKL) and representative Fab fragments (PDB 6XCA or 7K8P) with CDR3 loops removed were fit by rigid body docking into the cryo-EM density maps. a,f, C669; b,g, C643; c,h, C603; d,i, C601; e,j, C670; k,m, C666; and l,n, C663. RBD residues K417, N439, N440, E484, and N501 are highlighted as red surfaces. The N343 glycan is shown as a teal sphere. o, Composite model illustrating targeted epitopes of RBD-specific neutralizing mAbs (shown as VH-VL domains in colors from panels a-l) elicited from mRNA vaccines.
