Table 2.
Terminal glycotopes in the respiratory tract
| Glycotopea | Structurea | Mucus |
Respiratory tract |
Absent/N.D./traceb | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O-linked | O-linked | N-linked | |||
| sLeX | 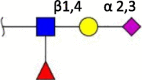 |
Human [39] | Human [38] Avian [37] |
Swine (N.D.) Ferret (N.D.) Horse (N.D.) Cow (N.D.) |
|
| Sda-epitope | 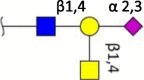 |
Ferret [35] | Ferret [35] | Human (trace) Swine (N.D.) Ferret (N.D.) Avian (N.D.) |
|
| NeuGc | 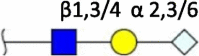 |
Cow [4] | Swine [34,36] | Human Avian Ferret (N.D.) |
|
| αGal-epitope |  |
Swine [34] | Swine [33,34,36] Ferret [35] Avian [75] |
Human | |
| Neu5Ac-O-Ac (4/7/8/9-O) |
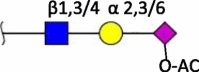 |
Human (9-O) [4] Horse (4-O/7-O/8-O/9-O/7,9-O) Cow (7-O/8-O/9-O/7,9-O) |
|||
| Neu5Gc-O-Ac (7/8-O) |
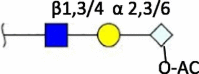 |
Swine (8-O) [4] Cow (7-O/8-O) |
|||
| 2,6SIA-LacdiNAc | 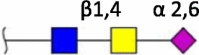 |
Ferret [35] | Human (N.D.) Swine (N.D.) |
||
| Sulfation (3S, 6S) | 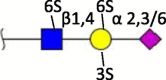 |
Human [39] | |||
Terminal structures at the non-reducing end of O- and N-linked glycan chains detected by mass spectrometry on epithelial cells or respiratory mucus in the indicated species. Differential expression at different locations along the respiratory tract has been analyzed in some cases but is not shown here. Neu5Ac (purple diamond), Neu5Gc (light blue diamond), N-acetylglucosamine (blue square), N-acetylgalactosamine (yellow square), galactose (yellow sphere), fucose (red triangle). S indicates sulfation.
Species in which a structure was not detectable (N.D.) or hardly detectable (trace) in extensive studies are indicated.
