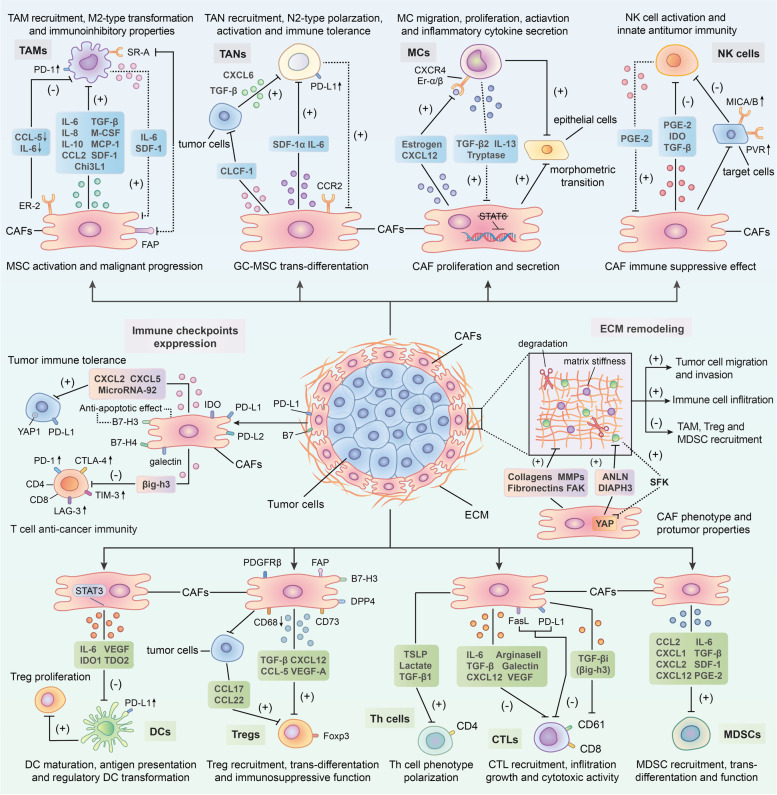
Fig. 2.
Crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and immune components in the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME). CAFs can orchestrate an immunosuppressive TME via interacting with the immune microenvironment in tumor. Through the secretion of multiple chemokines, cytokines and other effector molecules such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-X-C chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12), C–C chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), stromal-derived factor-1 (SDF-1), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) along with indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), CAFs modulate immune cells-mediated antitumor immunity through the following pathways: Promoting the trans-differentiation or polarization of immune cells such as tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), tumor-associated neutrophils (TANs), mast cells (MCs), dendritic cells (DCs) and T lymphocytes into certain protumorigenic cell subsets; Facilitating the activities of immune inhibitory cells in terms of recruitment, activation and immunosuppressive effects including M2-type TAMs, N2-type TANs, regulatory DCs (rDCs), regulatory T(Treg) cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs); Restricting the cytotoxic activity and cytokines production of effector immune cells like natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Notably, several infiltrating immune cells such as TAMs, TANs, MCs and DCs can in turn exert promoting effect on CAFs activation and function, thereby contributing to the formation of immune suppressive loops. Moreover, CAFs can also upregulate the expression of immune checkpoint molecules such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1)/programmed death receptor ligand-1 (PD-L1) and cytotoxic T lymphocyte associate protein-4 (CTLA4)/B7 in both themselves and other cells in the TME to induce T-cells dysfunction. Meanwhile, CAFs are able to remodel extracellular matrix (ECM) to facilitate immune suppression through the production of fibronectin, collagen and metalloproteinases (MMPs) as well as the activation focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling pathway. Finally, immune checkpoint molecule overexpression on CAF surface as well as matrix deposition around would inhibit CAF apoptosis and facilitate their activation and function