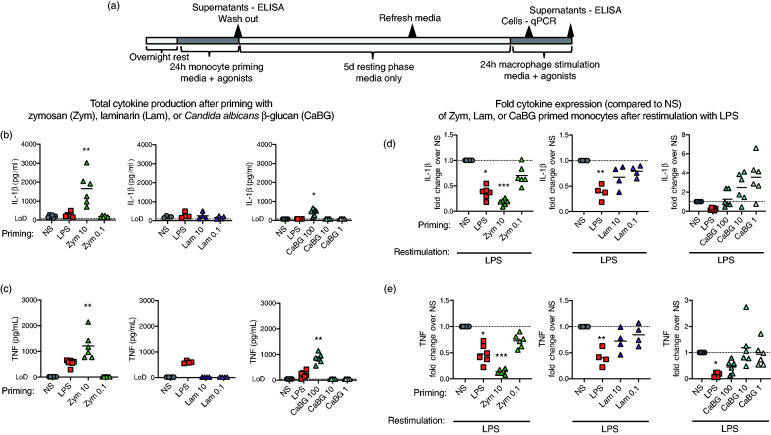
Figure 1.
β-Glucans induced a tolerized or trained phenotype in primary porcine monocytes. (a) In vitro monocyte culture scheme. Peripheral porcine monocytes (CD14+) were primed with zymosan (Zym; 0.1–10 µg/ml), laminarin (Lam; 0.1–10 µg/ml), β-glucan from C. albicans (CaBG; 1–10 µg/ml), LPS (0.1µg/ml), or non-stimulated (NS; media only) for 24 h, washed with warm PBS, and then cultured for 5 d in supplemented media (sMedia) with the sMedia refreshed at 3 d. After 5 d the cells were re-stimulated with LPS and supernatants (24 h) were collected for analysis of cytokine production. Total (b) IL-1β and (c) TNF-α production following Zym, Lam, or CaBG stimulation were measured by ELISA. Cytokine production for each priming group, following LPS re-stimulation were measured by ELISA and expressed relative to the media primed group (NS/LPS) for each pig, (d) IL-1β and (e) TNF-α. Data are presented as mean (bar) and significance (* P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001) as compared to unstimulated (NS) controls. A Friedman test (one-way ANOVA) was followed by a Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Data are representative of three independent experiments (n = 4–6 per study).