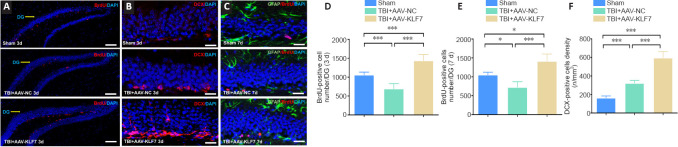
Figure 10.
KLF7 increases neural proliferation following TBI.
(A–C) Immunofluorescence staining of BrdU (proliferating neurons, red, stained by Alexa 555), DCX (newly generated neurons, red, stained by Alexa 555), and GFAP (astrocytes, green, stained by fluorescein isothiocyanate) with nuclear staining (DAPI; blue) in the ipsilateral hippocampus dentate gyrus (DG) in the three groups at 3 and 7 days following TBI. Compared with the TBI + AAV-NC group, BrdU-positive cells increased in the TBI + AAV-KLF7 group at 3 and 7 days following TBI. DCX-positive cells exhibited a similar pattern of change under the different treatment conditions. Scale bars: 100 μm in A, 200 μm in B and C. (D, E) Quantification of the number of BrdU-positive cells in the DG at 3 (D) and 7 (E) days following TBI. (F) Quantification of the density of DCX-positive cells at 3 days following TBI. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 4). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). AAV: Adeno-associated virus; BrdU: 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine; DAPI: 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DCX: doublecortin; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; KLF7: Krüppel-like factor 7; NC: negative control; TBI: traumatic brain injury.