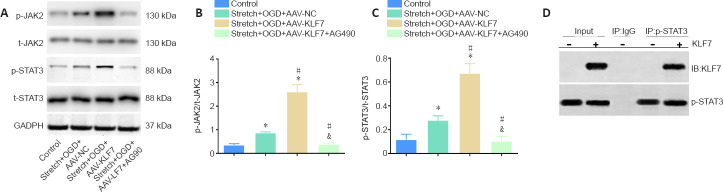
Figure 4.
Involvement of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in the neuroprotective effects of KLF7.
(A) Representative western blot of p-JAK2, t-JAK2, p-STAT3, and t-STAT3 expression in cultured HT22 cells at 1 day after stretch and OGD treatment. (B, C) Quantitative results of the relative optical densities of p-JAK2/t-JAK2 and p-STAT3/t-STAT3. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of the interactions between KLF7 and p-STAT3 in stretch- and OGD-damaged HT22 cells at 1 day, revealing a physical interaction between KLF7 and p-STAT3. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. Each experiment was repeated three times. *P < 0.05, vs. control group; #P < 0.05, vs. stretch + OGD + AAV-NC group; &P < 0.05, vs. stretch + OGD + AAV-KLF7 group (one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test). AAV: Adeno-associated virus; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IB: immunoblotting; IP: immunoprecipitation; KLF7: Krüppel-like factor 7; NC: negative control; OGD: oxygen-glucose deprivation; p-JAK2: phospho-Janus kinase 2; t-JAK2: total-Janus kinase 2; p-STAT3: phospho-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; t-STAT3: total-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.