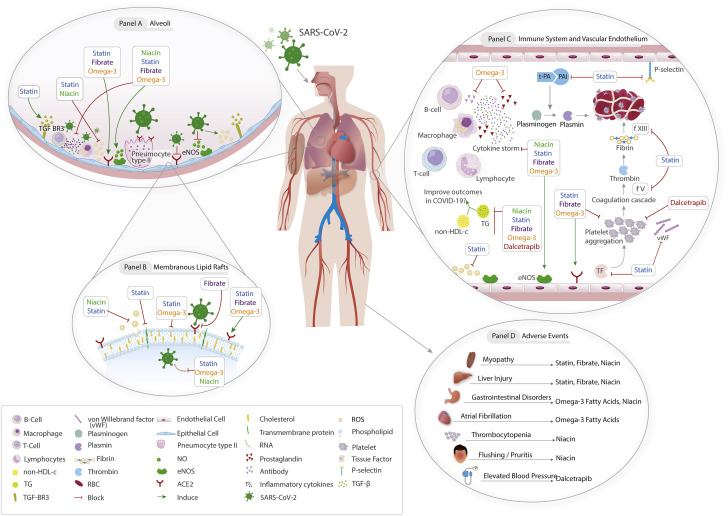
Figure 2.
Posited Mechanisms of Action of Lipid-Modulating Agents in COVID-19
(A) Binding of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) to pneumocytes results in cytokine release. Statins, fibrates, and omega-3 fatty acids can maintain the alveolar epithelial integrity. Statins may alleviate pulmonary fibrosis. (B) Fibrates, statins, and omega-3 fatty acids can inhibit viral entry. (C) Omega-3 fatty acids can inhibit the excessive antibody release. Statins, fibrates, omega-3 fatty acid, and dalcetrapib may have antiplatelet activities. Statins may also have antithrombotic properties. (D) Possible adverse effects of lipid-modulating agents. ACE = angiotensin-converting enzyme; COVID-19 = coronavirus disease-2019; CYP = cytochrome P450; RBD = receptor-binding domain; TG = triglyceride.