FIGURE 1.
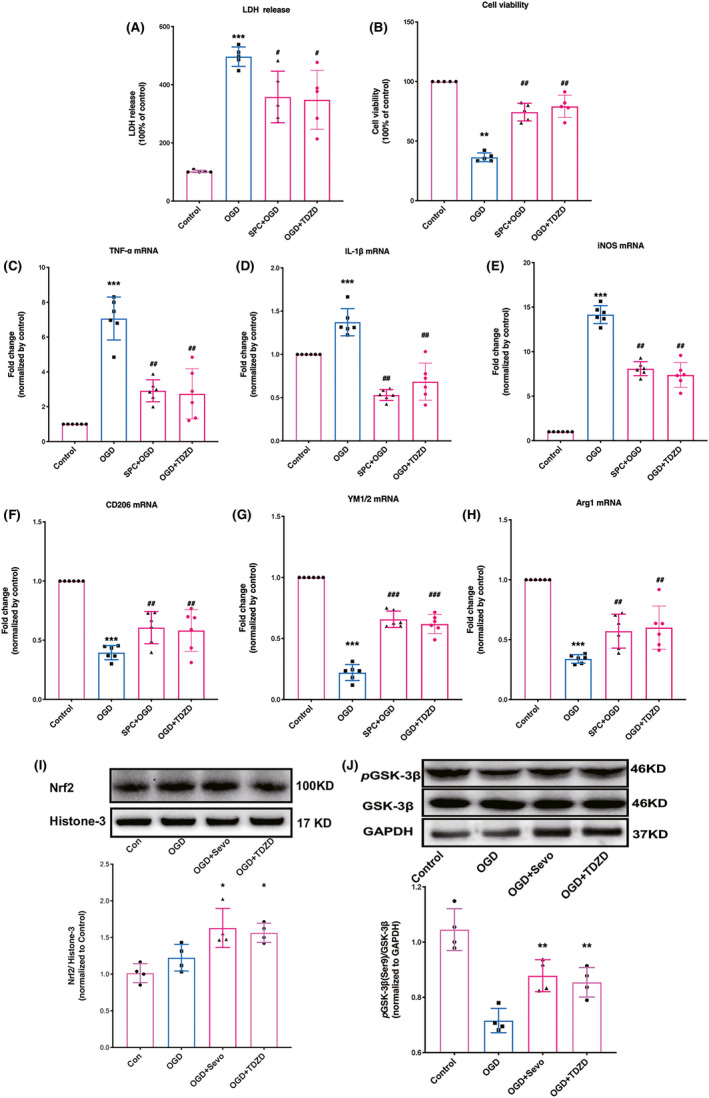
SPC and TDZD shifted microglia/macrophages polarization toward anti‐inflammatory phenotype, increased Nrf2 nuclear expression and GSK‐3β phosphorylation after OGD challenge. (A, B) Effect of SPC and TDZD on cell viability (A) and plasma lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release levels in primary cortical microglia after OGD (B). (C–E) The mRNA expression of pro‐inflammatory cytokines (TNF‐α, IL‐1β, and iNOS) 24 h following OGD. (F–H) The mRNA levels of anti‐inflammatory cytokines (CD‐206, YM1/2, arginase‐1) 24 h following OGD. (I) Western blot analysis for Nrf2 nuclear expression. (J) Western blot analysis for the phosphorylation of GSK‐3β. (n = 4). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 versus the control group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 versus OGD. One‐way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test was used for statistical analysis. IL‐1β, Interleukin‐1β; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; OGD, oxygen‐glucose deprivation; Sevo, sevoflurane preconditioning; TNF‐α, Tumor necrosis factor‐α
