FIGURE 1.
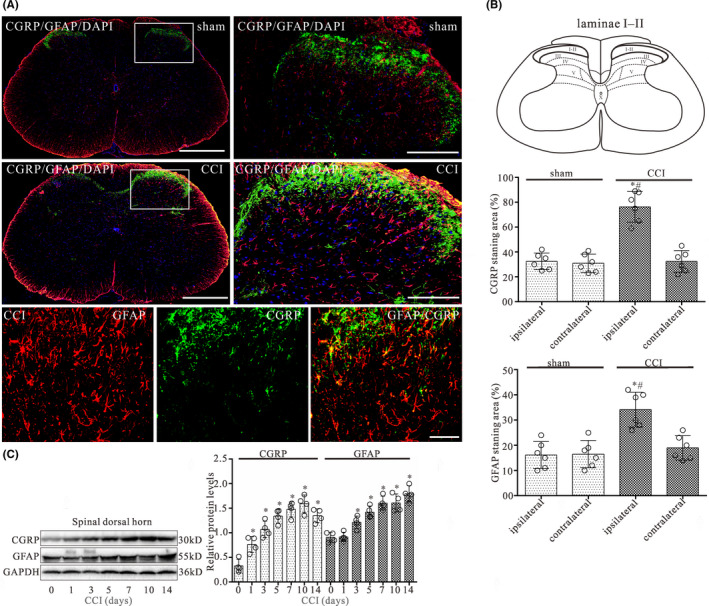
CCI evokes increases in the expression of CGRP and GFAP in the L4‐L5 spinal dorsal horn of CCI rats. (A) Double‐staining immunofluorescent images showing CGRP‐positive fibers (green) and GFAP (astrocyte maker)‐positive astrocytes (red) in the dorsal horn of sham and CCI groups on day 14 after surgery. The second column of first two rows is the higher magnification images indicated in the white boxes in the first column of first two rows. Cell nuclei were stained with the DAPI (blue). Note that numerous varicose nerve terminals immunoreactive for CGRP (green) closely approached GFAP‐immunopositive astrocytes (red) in the laminae I and II of spinal dorsal horn (third row). Scale bar 500 μm in the first column and 200 μm in the second column of the first two rows, 10 μm in third row. (B) Quantitative analyses of the percentages of CGRP‐immunoreactive surface in laminae I and II and GFAP‐immunostaining surface in spinal dorsal horn showed the CCI‐induced changes. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 6). *p < 0.05 versus sham‐ipsilateral; #p < 0.05 versus CCI‐contralateral. (C) Western blot analyses of CGRP and GFAP expression in the dorsal quadrant of L4‐L5 spinal segment ipsilateral to the operation side on 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 day after CCI surgery, respectively. The mean optic densities of the protein were calculated by normalizing to GAPDH. All values are expressed as the means ± SEMs (n = 4).*p < 0.05 versus sham group
