FIGURE 3.
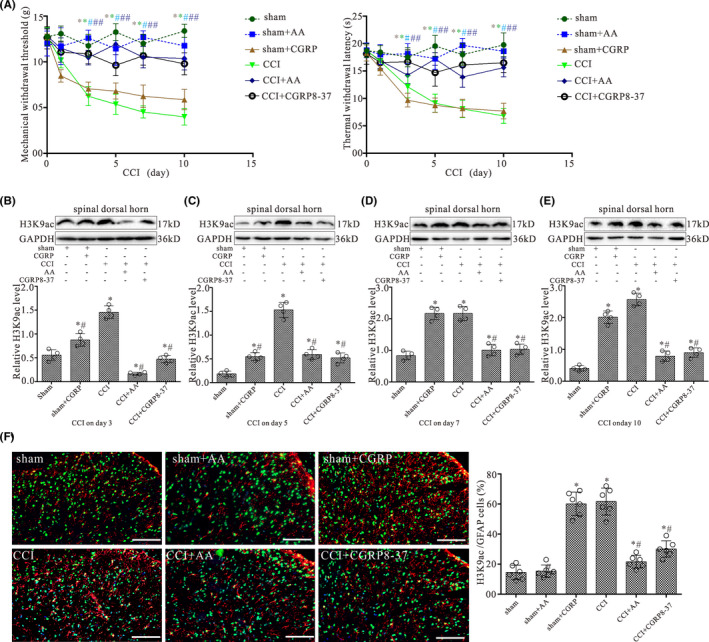
Intrathecal CGRP antagonist and HAT inhibitor administration prevent the pain hypersensitivity and attenuate increased levels of H3K9ac in the spinal dorsal horn induced by CCI. (A) Shows the mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) and thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) during the 10‐day observation period in rats treated with daily intrathecal injection of either 1 μM CGRP, 20 μM AA (HAT inhibitor), 2 μM CGRP8‐37, or vehicle in 10 μl for 9 days. All values are expressed as the means ± SEMs (n = 6). (B–E) Western blot analyses for H3K9ac protein levels in the dorsal quadrant of L4‐L5 spinal segment ipsilateral to the operation side with CCI surgery for 3, 5, 7, and 10 days, respectively. Data were obtained from animals treated with daily intrathecal injection of either 1 μM CGRP, 20 μM AA, 2 μM CGRP8‐37, or vehicle in 10 μl for 2, 4, 6, and 9 days, respectively. The mean optic densities of the proteins were calculated by normalizing to GAPDH. All values are expressed as the means ± SEMs (n = 4).*p < 0.05 versus sham groups; #p < 0.05 versus CCI alone groups. (F) Double‐staining immunofluorescent images showing the expression of H3K9ac (green) in astrocytes (GFAP, red) of L4‐L5 spinal dorsal horn ipsilateral to the operation side in the sham, sham + AA, sham + CGRP, CCI, CCI + AA, and CCI + CGRP8‐37 groups on day 10 after surgery, respectively. Scale bar 100 μm. Graph showing the percentages of GFAP/H3K9ac double‐labeled cells in L4‐L5 spinal dorsal horn of the sham, sham + AA, sham + CGRP, CCI, CCI + AA, and CCI + CGRP8‐37 groups, respectively. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 6). *p < 0.05 versus sham groups; #p < 0.05 versus CCI alone groups
