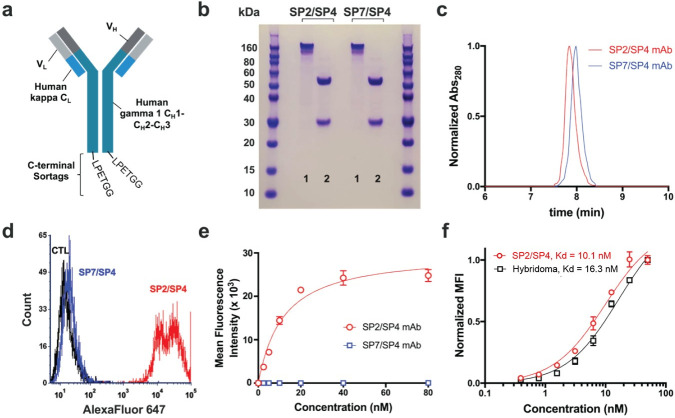
Fig 3. Characterization of recombinant mAbs.
(a) Schematic of recombinant mAb constructs. VL sequences were cloned in frame with human kappa CL, while VH was cloned in frame with human CH1-CH3. The sortag sequence, LPETGG, was appended at the C-terminus, immediately after the CH3 domain. (b) SDS-PAGE of recombinant mAbs, 1 = non-boiled, non-reduced, 2 = boiled, reduced. (c) Size exclusion HPLC of SP2/SP4 and SP7/SP4 mAbs, showing a single peak on the A280 detector at the expected size for immunoglobulin (7.9 min). (d) Flow cytometry histogram showing binding of 20 nM SP2/SP4 recombinant mAb, but not 20nM SP7/SP4 mAb, to Cho-hCD63-eGFP cells. (e) Flow cytometry-based binding curve of Cho-hCD63-eGFP cells (neither mAb showed any binding to Cho WT cells). (f) The affinity of SP2/SP4 mAb was similar to that of H5C6 hybridoma-derived monoclonal antibody (n = 3).