Figure 3.
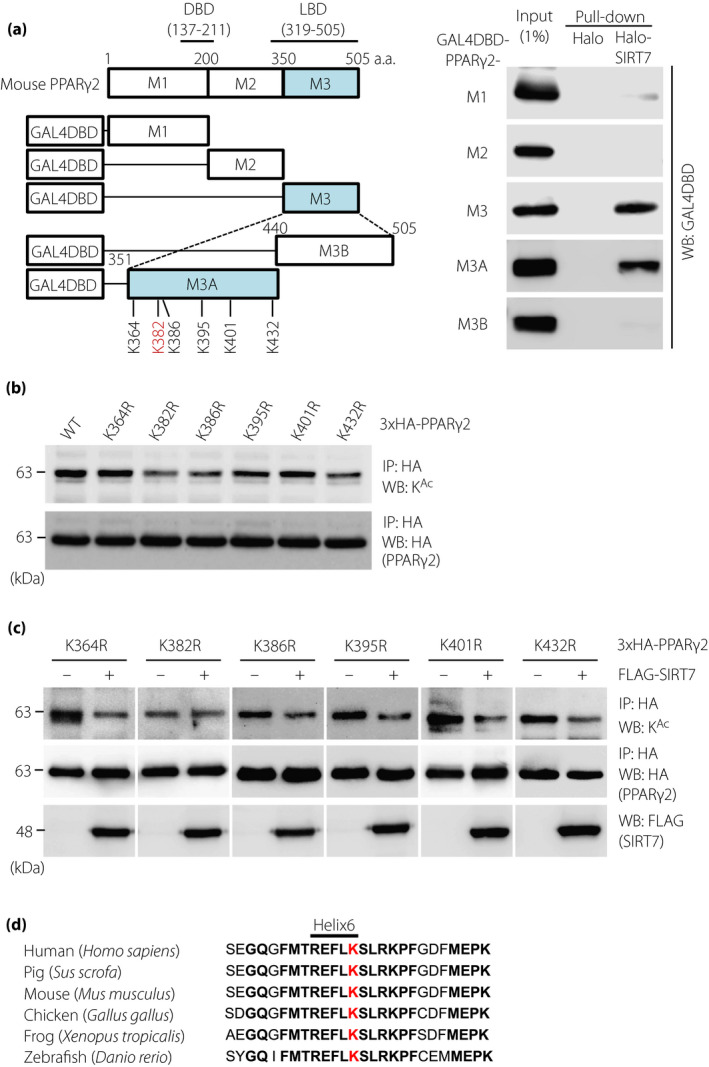
K382 is a target of the SIRT7‐mediated deacetylation of PPARγ2. (a) Mapping of SIRT7‐interacting sites in PPARγ2 by a pull‐down assay. Schematic diagrams of GAL4DBD‐fused mouse deletion mutants of PPARγ2, namely, M1 (1–200), M2 (201–350), M3 (351–505), M3A (351–439), and M3B (440–505), are illustrated on the left side. Halo‐SIRT7‐FLAG pull‐down assay with lysates from HEK293T cells expressing the indicated PPARγ2 deletion mutants fused with GAL4DBD (right). (b) Acetylation of KR mutants of PPARγ2. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated 3×HA‐PPARγ2 expression vectors. PPARγ2 acetylation was examined by immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis. (c) Effect of SIRT7 on the acetylation of the PPARγ2 KR mutants. HEK293T cells were transfected with PCAF and the indicated expression plasmids. PPARγ2 acetylation was examined by immunoprecipitation and western blot analysis. (d) Alignment of the PPARγ2 LBD from different species. The K382 of mouse PPARγ2 (red) is highly conserved in the indicated vertebrates
