Figure 5.
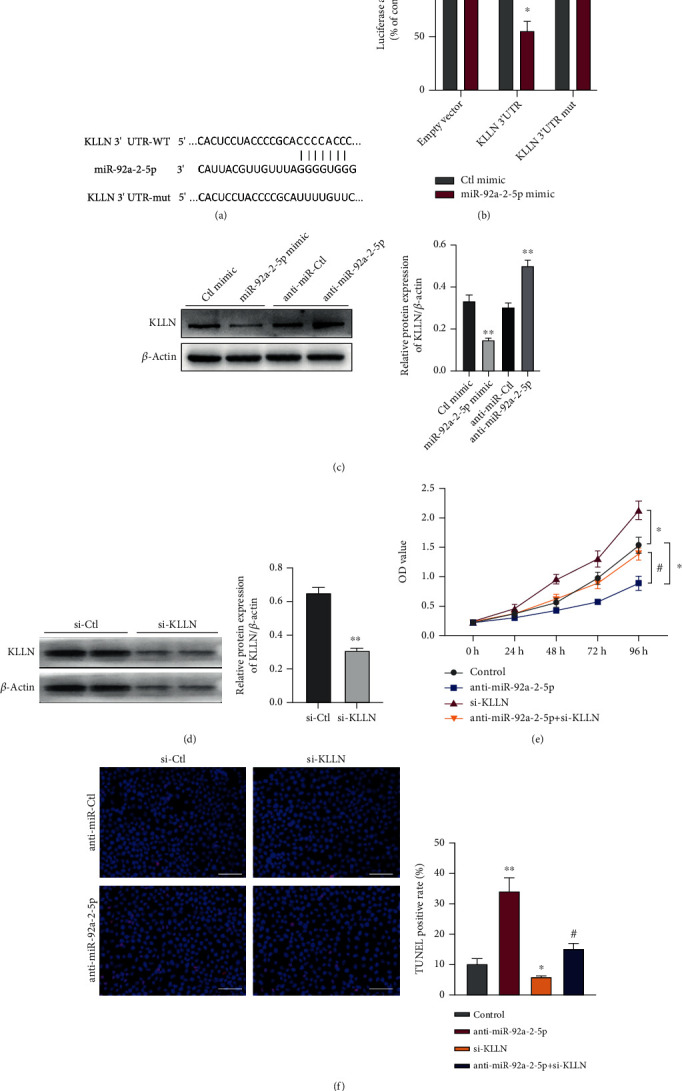
KLLN is a direct target of miR-92a-2-5p in the RCC cell. (a) Prediction of the miR-92a-2-5p binding site in KLLN 3′ UTR. (b) Luciferase reporter assays analyzed luciferase activity in 786-O cells after cotransfecting with the miR-92a-2-5p mimic or Ctl mimic and pmir-GLO vector containing the wild-type or mutated miR-92a-2-5p-binding site (mut) at KLLN 3′ UTR. ∗p < 0.05 vs. Ctl mimic. (c) Western blotting detected KLLN protein levels in 786-O cells transfected with the miR-92a-2-5p mimic, anti-miR-92a-2-5p, or its corresponding control miR. ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. corresponding control groups. (d) Western blotting detected KLLN protein levels in 786-O cells transfected with KLLN-specific siRNA (si-KLLN) or control siRNA (si-Ctl). ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. si-Ctl. (e) CCK-8 assay examined cell proliferation in 786-O cells after transfection with anti-miR-92a-2-5p or si-KLLN or cotransfection with both. ∗p < 0.05 vs. control group; #p < 0.05 vs. anti-miR-92a-2-5p group. (f) TUNEL assay detected cell apoptosis in 786-O cells treated as (e). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. control group; #p < 0.05 vs. anti-miR-92a-2-5p group (scale bars = 50 μm). Graph bars represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
