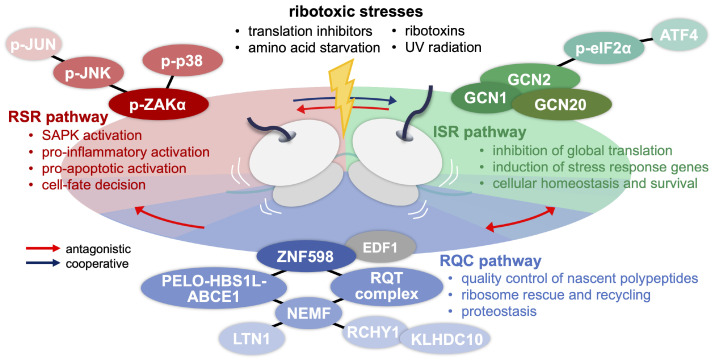
Fig. 2.
Ribosomal collisions trigger RQC, ISR, and RSR pathways. Ribotoxic stresses induce ribosomal collisions, and their distinct quality (e.g., scale, kinetics) and molecular signatures (e.g., structural changes in the collided ribosomes) may lead to differential activation of the three ribosomal surveillance pathways. RQC is responsible for the tonic control of ribosomal stalling and the quality expression of nascent chains to sustain proteostasis. ISR shuts down general translation via GCN2-dependent eIF2α phosphorylation upon global ribosome collisions while elevating the homeostatic stress response for cell survival. ZAK-initiated RSR activates SAPKs (i.e., JNK and p38) via the MAPK cascade, stimulating pro-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic pathways for cell-fate decisions. Antagonistic or cooperative crosstalks among the three ribosomal surveillance pathways have been documented and depicted accordingly.