Fig. 1. Increased anxiety- and depression-like phenotype of p11 KO mice.
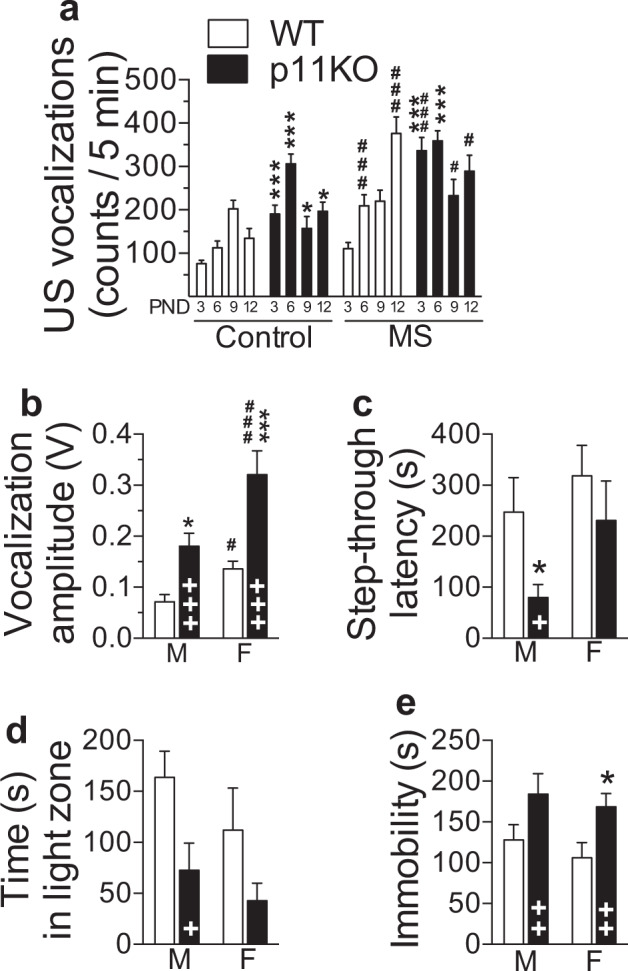
a P11KO pups display increased ultrasonic vocalizations (USVs). The number of USVs over a period of 5 min was recorded at PND3, 6, 9, and 12 in wild-type (WT) and p11 knockout (p11KO) pups (mixed sex, see Supplementary Information). Significant effects of genotype (p < 0.001, F(1,134) = 38.38), rearing (p < 0.001, F(1,134) = 46.5) and age (p = 0.0001, F(3,392) = 7.14) as well as genotype × age (p < 0.001, F(3,392) = 23.99), rearing × age (p < 0.01, F(3,392) = 4.92) and genotype × rearing × age (p < 0.01, F(3,392) = 5.33) interaction. All data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, versus corresponding WT; #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001, rearing difference within genotype; calculated by three-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test. PND postnatal day. b Sound intensity of vocalizations was measured over 5 s immediately post-shock in the training trial of the passive avoidance (PA) test. P11KO mice vocalized more intensely (louder) after a mild electric shock exposure during PA training. Significant effects of genotype (p < 0.0001, F(1,29) = 21.75) and sex (p < 0.0001, F(1,29) = 20.10). c Step-through latency in the passive avoidance retention test 24 h following training was lower in p11KO mice (p < 0.05, F(1,34) = 6.17). d Time spent in the light compartment of the 5-min light–dark exploration test indicated an anxiety-like phenotype in p11KO mice of both sexes (genotype effect, p < 0.05, F(1,32) = 6.83). e Cumulative immobility time (floating) in the forced swim test confirmed a depressive-like phenotype in p11KO mice (p < 0.01, F(1,31) = 9.28). All data represent mean ± SEM. +p < 0.05, ++p < 0.01, +++p < 0.001 overall genotype difference; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, versus corresponding WT; #p < 0.05, ###p < 0.001, sex difference within genotype; calculated by two-way ANOVA, followed by Fisher’s LSD test.
