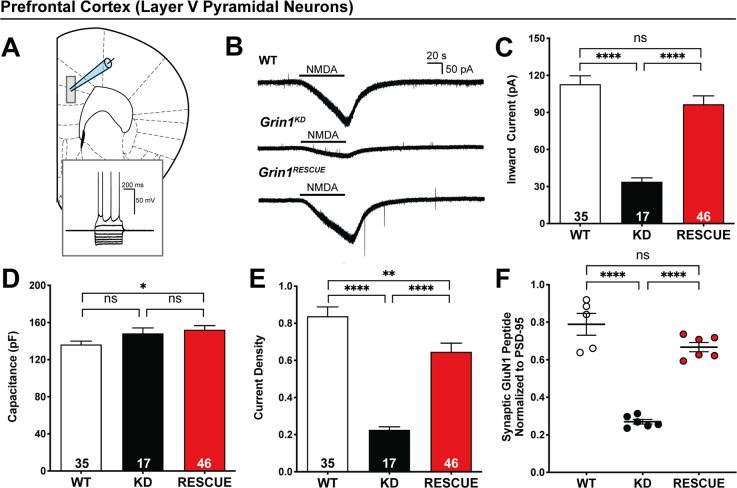
Fig. 3. NMDAR currents and synaptic GluN1 peptide levels are restored in the mPFC of Grin1RESCUE mice.
a Schematic of mPFC with whole cell patch clamp recording from layer V adapted from [48]. Inset: electrophysiological signature of Grin1RESCUE layer V pyramidal neuron. b Representative traces in voltage clamp (−75 mV) showing prefrontal response to NMDA across the three genotypes (number of layer V pyramidal neurons shown, 5–6 mice per genotype). c Quantification of peak amplitude of prefrontal NMDAR-elicited currents. One-way ANOVA, effect of genotype, F2,95 = 22, p < 0.0001, Bonferroni post hoc. d Capacitance of prefrontal layer V pyramidal neurons. One-way ANOVA, Bonferroni post hoc. e Current density of prefrontal NMDA-elicited currents. One-way ANOVA, effect of genotype, F2,95 = 3.6, p = 0.03, Bonferroni post hoc. f Synaptic GluN1 peptide (IVNIGAVLSTR) levels in the PFC. One-way ANOVA, effect of genotype, F2,14 = 64.76, p < 0.0001, Bonferroni post hoc. All data shown as mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001, ns not significant.