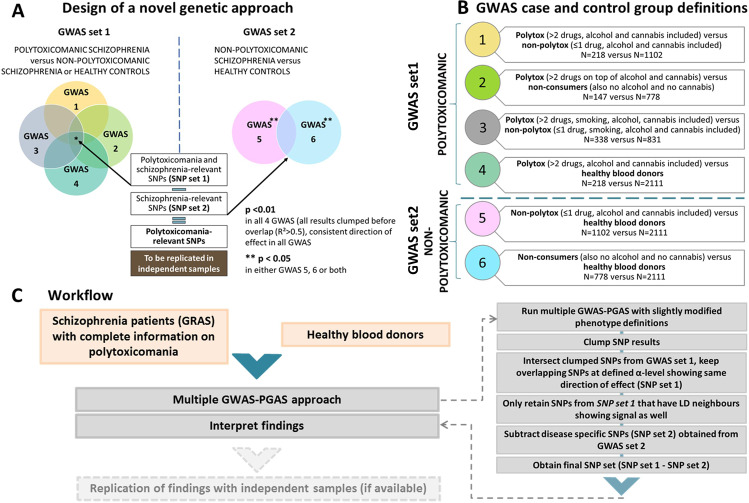
Fig. 3. Novel multiple GWAS–PGAS approach.
A Overview of the analysis design. GWAS set 1 to obtain SNP set 1: 4 GWAS contrasting polytoxicomanic versus non-polytoxicomanic individuals (including healthy individuals) with slightly varied phenotype definitions (details in (B)) to identify SNPs that show consistent associations (p < 0.01) in all 4 GWAS. These SNPs are considered polytoxicomania and/or schizophrenia-associated. GWAS set 2 to obtain SNP set 2: SNPs associated exclusively with schizophrenia, but not polytoxicomania, resulting from GWAS 5 and/or 6 (p < 0.05) are subtracted from SNP set 1 (polytoxicomania and/or schizophrenia-associated), yielding the final set of polytoxicomania-relevant SNPs. B Diagram showing exact phenotype definitions and sample sizes per group for GWAS 1–6. C Detailed workflow of the novel GWAS–PGAS approach including clumping procedure to reduce number of SNPs in the final set.