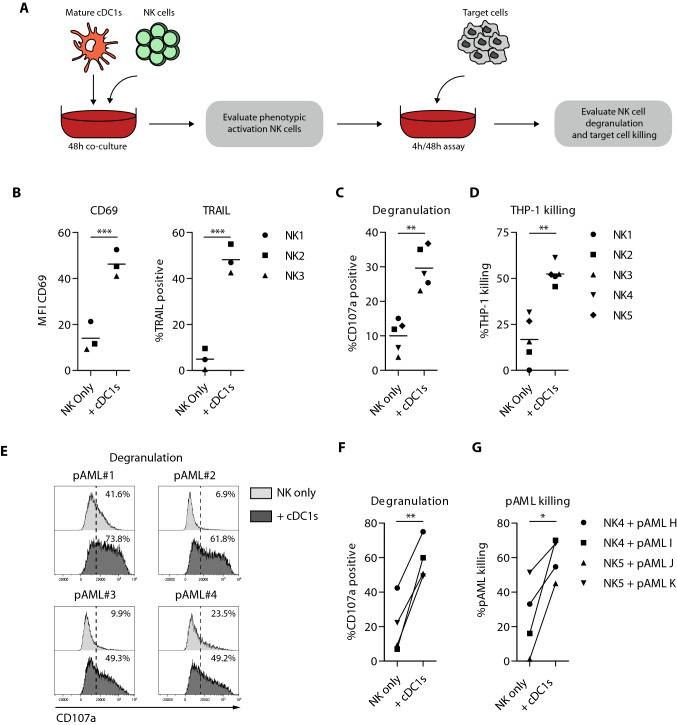
Fig. 6.
Ex vivo-generated cDC1s effectively enhance NK cell leukemia reactivity. a Schematic overview of NK cell activation, degranulation and killing assays. Mature ex vivo-generated cDC1s were co-cultured with NK cells (1:1) for 48 h, followed by evaluation of phenotypic NK cell activation. Additionally, 48 h cDC1-activated NK cells were cultured with the AML cell line THP-1 for 4 h or primary AML cells for 48 h, whereupon NK cell degranulation and target cell killing were evaluated. b MFI of CD69 and expression of TRAIL on cDC1-activated NK cells after 48 h co-culture and prior to 4/48 h degranulation and killing assay. Lines indicate mean value (n = 3 independent NK cell donors). c, d Degranulation by (c) and killing of THP-1 cells (d) by cDC1-activated NK cells. Lines indicate mean value (n = 5 independent NK cell donors). e–g Degranulation by (e, f) and killing of primary AML cells (g) by cDC1-activated NK cells. Lines indicate mean value (n = 4). Statistical analysis was performed using paired T test (b–d, f and g). ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *P < 0.05. NK, natural killer; pAML, primary acute myeloid leukemia; MFI, median fluorescence intensity; TRAIL; TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand