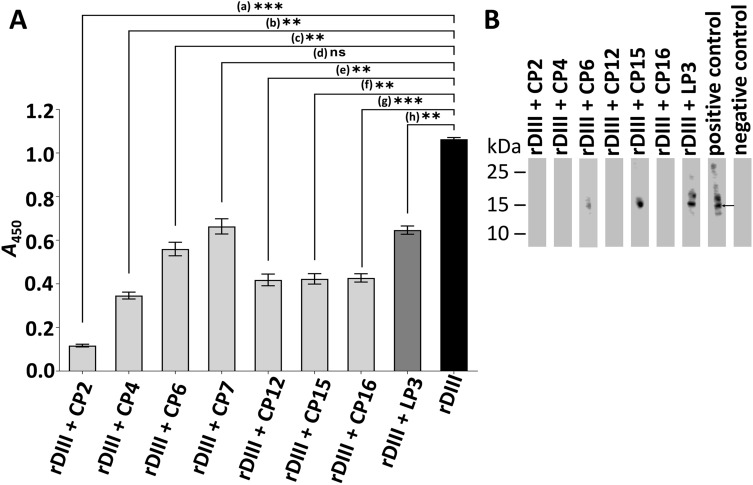
Figure 4.
Assessment of the blocking ability of peptides on proteins of hBMECs. (A) Blocking of the interaction between proteins of hBMECs and rDIII by ELISA. Proteins of hBMECs were coated into microtiter wells. Data present mean of triplicates with ± S.D after subtraction of negative control (rDIII excluded from the assay). A statistically significant difference (P < 0.01, two-tailed P-value, GraphPad Prism v8.4.3.) was calculated by paired t-test compared to the positive control (interaction between rDIII and hBMECs proteins). a: P = 0.0002; b: P = 0.0010; c: P = 0.0058; d: P = 0.0101 (ns); e: P = 0.0015; f: P = 0.0017; g: P = 0.0004; h: P = 0.0021. A – Absorbance. (B) Blocking of the interaction between proteins of hBMECs and rDIII by Western blot. Arrow shows interaction between rDIII and ~ 15 kDa receptor of hBMECs. Positive control – unblocked rDIII incubated hBMECs proteins. Negative control – rDIII was omitted from the protocol. rDIII – recombinant DIII; CP – 7-mer cyclic peptide; LP – 12-mer linear peptide.