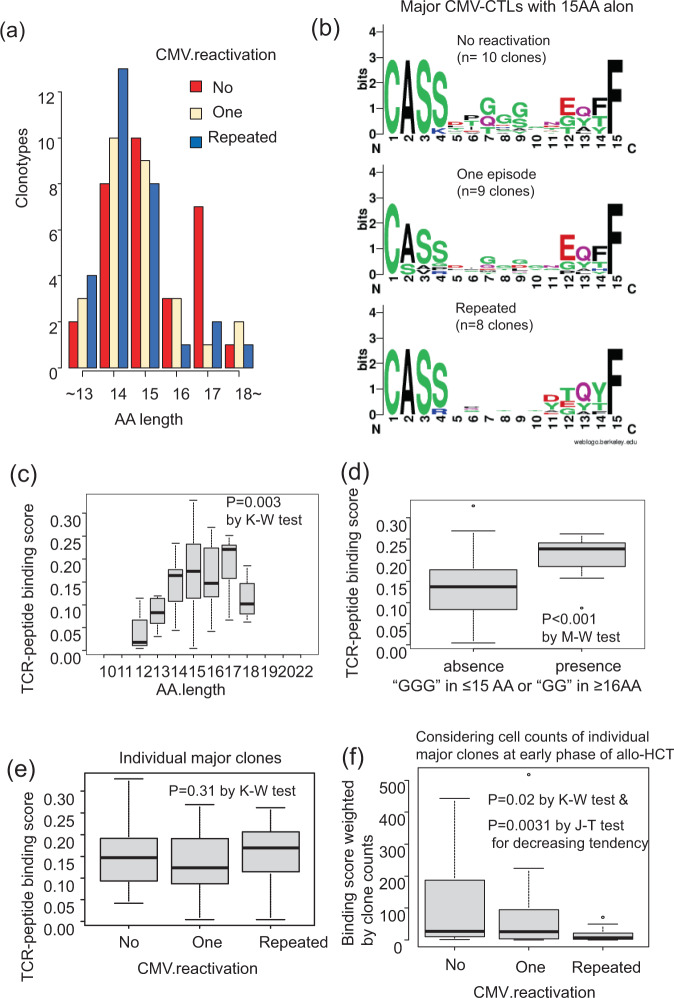
Fig. 2. Amino acid (AA) sequence logos and AA length in the major HLA-A24-restricted CMV-pp65-specific cytotoxic T-cell (CMV-CTL) clones accounting for >5% of all CMV-CTLs within individual recipients in the early or late phases after allo-HCT.
a AA length according to CMV-reactivation pattern: no-CMV reactivation (n = 10), one-episode (n = 9), and repeated reactivation (n = 7) groups. The AA length of TCRβ-CDR3 decreased in the following order: no-CMV reactivation > one-episode (n = 9) > repeated CMV reactivation groups (P = 0.015 by the Jonckheere–Terpstra (J–T) test for decreasing tendency). b AA sequence logos of TCRβ-CDR3 in the major CMV-CTLs with 15 AA-long CDR3-TCRβ according to the CMV-reactivation pattern. c Difference in TCR-peptide binding scores among the major clones according to AA length of CDR3-TCRβ (P = 0.003 by the Kruskal–Wallis (K–W) test). d Difference in TCR-peptide binding scores among the major clones according to the presence of “(G)GG” motifs in CDR3-TCRβ (P < 0.001 by the Mann–Whitney U (M–W) test). e Difference in TCR-peptide binding scores among the major clones according to the CMV-reactivation pattern (P = 0.31 by the K–W test). f Difference in binding score weighted by the individual clone counts among the major clones in the early phase of allo-HCT according to the CMV-reactivation pattern (P = 0.02 by the K–W test, and P = 0.0031 by the J–T test for decreasing tendency). Individual box and whisker plots were constructed by the 25th percentile (Q1), median, and 75th percentile (Q3) with whiskers of 1.5 times interquartile range (IQR) lengths.