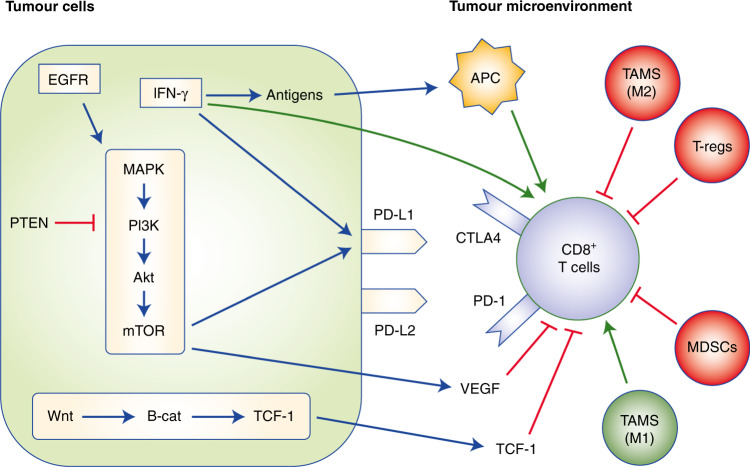
Fig. 2. The impact of intracellular tumour cell pathways and the tumour microenvironment on cytotoxic T cells in gastro-oesophageal cancer.
The figure depicts the various influences on cytotoxic T-cell function relating to the signalling pathways within the tumour itself as well as the tumour microenvironment (TME). EGFR epidermal growth factor receptor, IFNy interferon y, PTEN phosphatase and tensin homologue, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase, PI3K phosphoinositide 3-kinases, β-cat β-catenin, TCF-1 T-cell factor 1, APC antigen-presenting cell, VEGF vascular-endothelial growth factor, MDSCs myeloid-derived suppressor cells, TAM tumour-associated macrophages, PD-L1 programmed death ligand 1, PD-L2 programmed death ligand 2, CTLA-4 cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4.