Fig. 2.
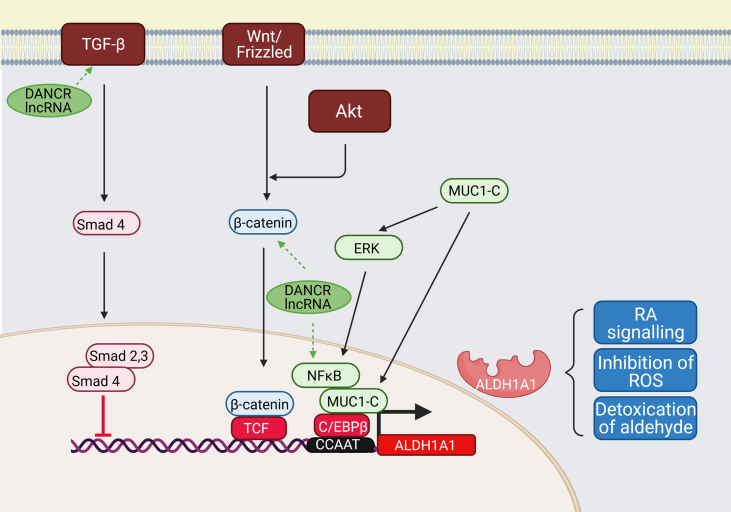
Transcriptional regulation of ALDH1A1.
ALDH1A1 promoter can be activated by several molecular pathways: 1) Wnt pathway regulating ALDH1A1 through β-catenin and T-cell factor (TCF)-dependent transcription; 2) Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) - downregulating ALDH1A1 in Smad4-dependent manner; 3) Mucin 1-C (MUC1-C) inducing extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signalling and phosphorylating CCAAT enhancer-binding protein (C/EBPβ), which leads to induction of ALDH1A1 expression.
TGF-β. Negative regulation of ALDH1A1 by TGF-β through Smad4 binding was shown in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Suppression of Smad4 by specific si-RNA upregulated the expression of ALDH1A1, and overexpression of Smad4 downregulated it, leading to the decrease of the ALDH+ population and their tumour-initiating activity [40].
Wnt/ β- catenin. Suppression of β-catenin through specific siRNA resulted in a reduction of the ALDH+ cell population of prostate cancer progenitors. It sensitized it to radiation, proving that the Wnt pathway directly regulates ALDH1A1 through β-catenin/TCF dependent transcription [41]. Following study of ALDH+ cervical cancer cells revealed that ALDH expression could be triggered by β-catenin through a Wnt/Frizzled-independent mechanism, and this effect is downstream of AKT activity. Pharmacological inhibition of AKT reduced the active form of the β-catenin and inactive form of GSK3 in ALDH+ cells and reduced ALDH protein level and activity [42].
Mucin 1. In breast cancers, MUC1-C induced ERK-mediated phosphorylation and activation of the C/EBPβ transcription factor, forming the complex on the ALDH1A1 promoter and activating it. [43].
Long ncRNA. The effect of DANCR is described in Fig. 3.
Abbreviations: C/EBPβ - CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β, ERK - extracellular signal-regulated kinase, GSK3 - glycogen synthase kinase-3, TCF - T-cell factor, TGF-β - Transforming growth factor β.