FIGURE 9.
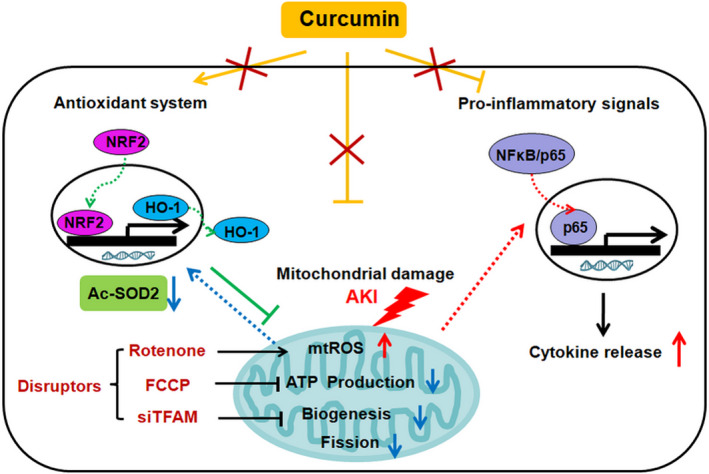
The proposed findings of this study. CUR exerts multiple benefits in AKI, including its antioxidant (induction of NRF2/HO‐1 pathway and SOD2 deacetylation), anti‐inflammatory (inhibition of NFκB activation and cytokine release) and mitochondrial protective (reduction in mtROS and mitochondrial fragmentation, increase in biogenesis and ATP synthesis) effects. However, mitochondrial disruption by ETC inhibitors or siTFAM markedly reduced the antioxidant and anti‐inflammatory potential of CUR. This study indicates that mitochondrial damage is a driver of AKI and that the therapeutic role of CUR in AKI is primarily dependent on mitochondrial pathways
