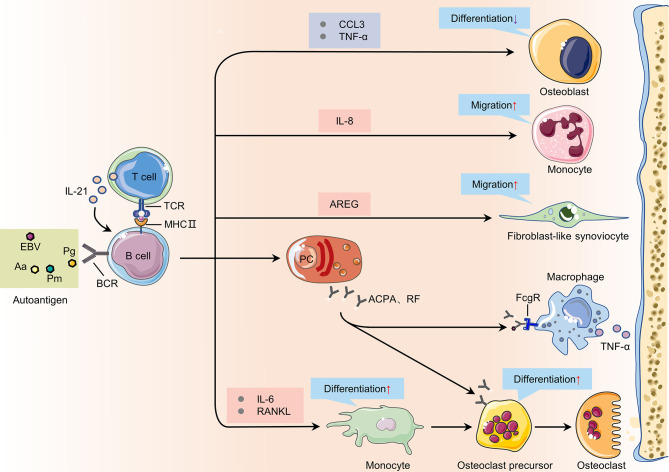
Figure 4.
The immunopathogenic role of B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. During the onset of RA, B cells can promote the activation, proliferation, and differentiation of other cells such as T cells, monocytes, and osteoclasts in the synovium by providing cytokines, autoantibodies and other mediators. TCR, T cell receptor; MHC II, major histocompatibility complex class II; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; FcgR, Fcgamma receptors; AREG, amphiregulin; RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; Pg, Porphyromonas gingivalis; Aa, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans; Pm, Proteus mirabilis; EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; PC, plasma cells.