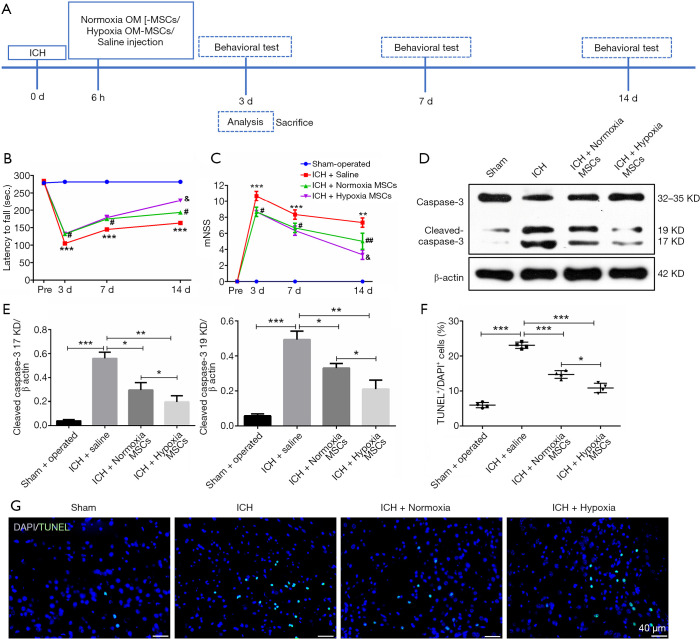
Figure 1.
OM-MSCs alleviated the neurological deficit and cell apoptosis in the in vivo model of ICH. (A) Schematic representation of the experimental protocol. (B) The rotarod test, and (C) the mNSS test were assessed before ICH and on day 3, 7, and 14 post-ICH. Data were expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=7/group at 3 days; n=5/group at 7 and 14 days) (***, P<0.001, **, P<0.01 vs. sham-operated; #, P<0.05, ##, P<0.01 vs. ICH + saline; &, P<0.05 vs. ICH + Normoxic MSCs). (D,E) Western blot images and densitometric analysis of caspase-3. (F) Quantification of TUNEL staining was expressed as (TUNEL-stained nuclei/DAPI-stained nuclei) × 100%. Sections were stained with DAPI (blue) to show all nuclei. TUNEL-positive cells were increased at 3 days after ICH, and were decreased by OM-MSC administration, especially hypoxic OM-MSCs. Data were expressed as the mean ± SEM (n=4) (*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001). (G) Representative images of TUNEL staining from the ipsilateral cortex of the perihematomal area. The scale bar is 40 µm. Abbreviations: OM-MSCs, olfactory mucosa mesenchymal stem cells; ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; mNSS, modified neurological severity score; SEM, standard error of mean; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-mediated dUTP Nick-end labeling; DAPI, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.