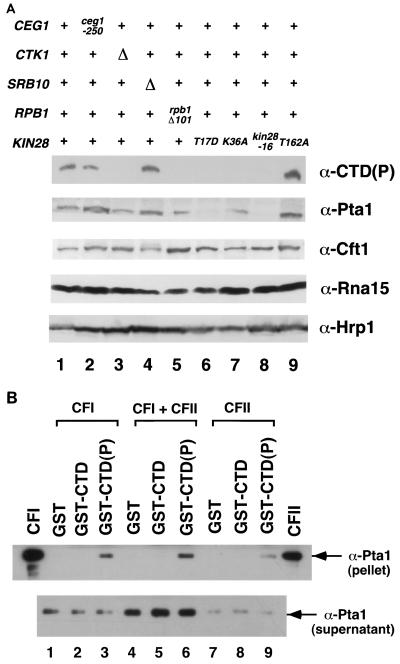
FIG. 6.
Interactions between the 3′ processing factor Pta1 and the phosphorylated CTD. (A) Pta1 protein levels are reduced in kin28 mutant strains. Whole-cell extracts were prepared from strains grown for 6 h at 30°C. Eighty micrograms of extract from each strain was assayed by immunoblotting with B3 [α-CTD(P)], anti-Cft1, anti-Pta1, anti-Rna15, and anti-Hrp1 antibodies. Lanes: 1, wild type, PY469; 2, ceg1-250, YSB491; 3, ctk1Δ, YSB653; 4, srb10Δ, YSB 652; 5, rpb1Δ101 (CTD truncation, 11 wild-type heptapeptide repeats), N398; 6 to 9, FOAR strains yielded from shuffling kin28 mutants (T17D, K36A, -16, and T162A, respectively) into YSB626, as described in the legend to Fig. 2. (B) Pta1 is specifically retained on the phosphorylated CTD. Partially purified polyadenylation factors were incubated with GST (lanes 1, 4, and 7), unphosphorylated GST-CTD fusion protein (lanes 2, 5, and 8), or phosphorylated GST-CTD(P) (lanes 3, 6, and 9). Beads were pelleted and washed, and bound proteins were assayed by immunoblotting with anti-Pta1 antibodies. The CFI and CFII lanes are positive controls.