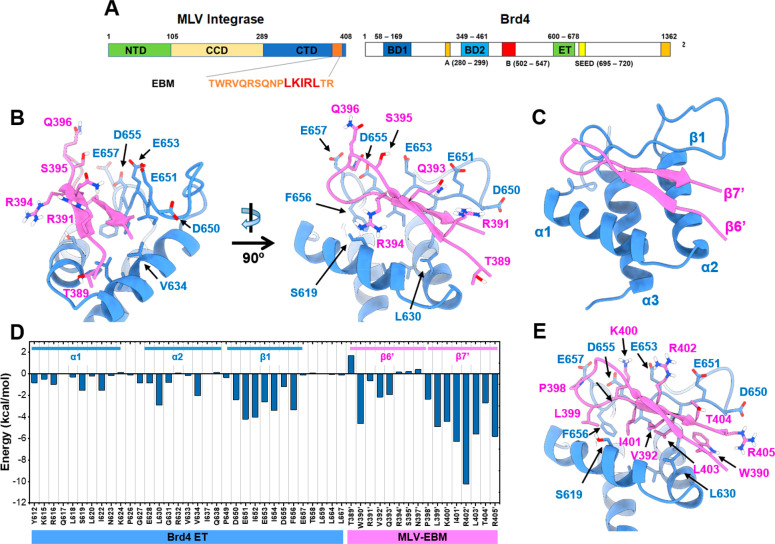
Figure 1.
Graphical illustration of amino acid residues at the MLV IN EBM-Brd4 ET domain interaction interface. (A) Schematic representation of MLV integrase (IN) and Brd4 (1–1342). Key domains and structural features are indicated for both: MLV IN C-terminal domain (CTD), catalytic core domain (CCD), and N-terminal domain (NTD). The ET-binding motif (EBM) is indicated in orange, and the location of LKIRL is highlighted in red. Brd4 bromodomains (BD1 and BD2), DNA binding motifs A and B, SEED domain, and extra-terminal domain (ET). (B) Representation of amino acids residue in the β6′ strand of EBM (pink) and their interaction with the Brd4 ET domain (blue). Two perspectives of view indicate that the highlighted residues are not extensively in contact with the ET domain. (C) Annotation of the secondary structure of the EBM β-sheet and ET domain (PDB Code: 2N3K). (D) MM/GBSA per-residue energy decomposition profile of the EBM-ET complex indicating that β7′ of EBM and β1 of ET predominantly contribute to the protein–protein interaction. (E) Binding mode of LKIRL (399′–403′) with the ET domain showing that the LKIRL sequence interacts extensively with β1 of ET.