Abstract
Background
Differences in genetics and microenvironment of LUAD patients with or without TP53 mutation were analyzed to illustrate the role of TP53 mutation within the carcinogenesis of LUAD, which will provide new concepts for the treatment of LUAD.
Methods
In this study, we used genetics and clinical info from the TCGA database, including somatic mutations data, RNA-seq, miRNA-seq, and clinical data. More than one bioinformatics tools were used to analyze the unique genomic pattern of TP53-related LUAD.
Results
According to TP53 gene mutation status, we divided the LUAD patients into two groups, including 265 in the mutant group (MU) and 295 in the wild-type group (WT). 787 significant somatic mutations were detected between the groups, including mutations in titin (TTN), type 2 ryanodine receptor (RYR2) and CUB and Sushi multiple domains 3(CSMD3), which were up-regulated in the MU. However, no significant survival difference was observed. At the RNA level, we obtained 923 significantly differentially expressed genes; in the MU, α-defensin 5(DEFA5), pregnancy-specific glycoprotein 5(PSG5) and neuropeptide Y(NPY) were the most up-regulated genes, glucose-6-phosphatase (G6PC), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and carry gametocidal (GC) were the most down-regulated genes. GSVA analysis revealed 30 significant pathways. Compared with the WT, the expression of 12 pathways in the mutant group was up-regulated, most of which pointed to cell division. There were significant differences in tumor immune infiltrating cells, such as Macrophages M1, T cells CD4 memory activated, Mast cells resting, and Dendritic cells resting. In terms of immune genes, a total of 35 immune-related genes were screened, of which VGF (VGF nerve growth factor inducible) and PGC (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator) were the most significant up-regulated and down-regulated genes, respectively. Research on the expression pattern of immunomodulators found that 9 immune checkpoint molecules and 6 immune costimulatory molecules were considerably wholly different between the two groups.
Conclusions
Taking the mutant group as a reference, LUAD patients in the mutant group had significant differences in somatic mutations, mRNA-seq, miRNA-seq, immune infiltration, and immunomodulators, indicating that TP53 mutation plays a crucial role in the occurrence and development of LUAD.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12890-021-01671-8.
Keywords: TP53, Lung adenocarcinoma, Mutation, Genome, Microenvironment
Background
According to the study in 2020, among all cancers, the mortality of lung cancer ranks first, with about 1.8 million death occurring, and the incidence of lung cancer ranks second, with more than 2.2 million new cases being diagnosed [1]. Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is the most frequent subtype [2], accounting for more than 40% of all lung cancers [3]. Despite considerable progress in both diagnosis and treatment, the five-year survival of patients with lung cancer remains very poor [4].
TP53, coding the supermolecule p53, is located on human chromosome 17p 13.1 and plays a vital role in controlling cell cycle progression, aging, DNA repair and senescence, cell death, and cell metabolism [5–7]. This function is achieved through its wild-type form. Once the TP53 gene is mutated, it loses its position as a tumor suppressor gene and promotes tumorigenesis at the same time [5, 8]. TP53 mutation is considered to be the most common kind of gene-specific changes in human cancers and occurs in almost every type of human tumours [9–11]. Unlike other tumor suppressors that are usually inactivated by frameshift or nonsense mutation, most of the TP53 mutation are missense mutation, and the same is true in lung cancer [9, 12]. Previous studies have shown that TP53 mutations can promote the metastasis of cancer cells [13], some important somatic mutations can affect the effectiveness of LUAD immunotherapy [14, 15]. In addition, abnormal TP53 is considered to be an important prognostic factor for no-small-cell carcinoma (NSCLC) [16]. However, to date, it is still unknown how TP53 mutation affects LUAD patients.
To study the effect of TP53 mutation on LUAD patients, we consistently analyzed changes in somatic mutation data, clinical data, immune infiltration data, and gene expression obtained from the TCGA database. This research will enhance our understanding of TP53 mutation in LUAD and offer a reference for future studies.
Materials and methods
Acquisition of LUAD expression data set
VarScan 2-based somatic mutation data were obtained from the TCGA website (https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/) (TCGA_LUAD), RNA and miRNA sequencing data, and corresponding clinical data were additionally extracted from this website. After matching with somatic mutation data, the RNA data of 523 patients, miRNA data of 509 patients, and clinical data of 509 patients were finally screened for future research between the groups with or without TP53 mutation of LUAD patients.
Somatic mutation analysis
According to TP53 gene mutation status, the somatic mutation data was divided into a wild-type group (WT, n = 295) and a mutant group (MU, n = 265). The “maftools” package in R (version 4.0.4) was applied to estimate the mutation rate of every gene [17]. The statistical significance threshold was set to an adjusted p-value of 0.05.
Summary statistics of clinical features
All clinical data were analyzed using SPSS statistical analysis software (version 23.0). In the group comparison of categorical variables, Pearson’s chi-square was used, with p-value = 0.05 as the cutoff [18].
Screening for differentially expressed genes (DEGs)
The original data from the TCGA database were screened by removing the data whose average expression value was less than 1 in all samples, the remaining data were normalized by a weighted trimmed average based on a logarithmic ratio method. To obtain DEGs between the groups, the mRNA expression data, miRNA expression data, and IncRNA expression data were analyzed using the R package “edgeR” [19]. Taking the |log2 fold change| > 1.0 and an adjusted p-value < 0.05 as the critical value to identify differentially expressed genes. To further investigate the relationship between DEGs, the protein-protein interactions (PPI) network, transcription factor regulatory network, and ceRNA network were constructed and analyzed [20]. Cytoscape software (version 3.7.1) was used to visualized all networks.
To identify the potential biological function differences between WT and MU, R package “clusterProfiler” was used to perform gene ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis on the differentially expressed mRNAs [21]. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was performed via GSEA (version 4.0.3), and Gene Set Variation Analysis (GSVA) was performed via the GSVA software package in the R [22].
Estimation of tumor immune infiltrating cells
To systematically quantify the proportions of immune cells in the TCGA_LUAD samples, we uploaded a modified TCGA RNA-seq dataset with standard annotation to the CIBERSOPT portal, and ran the LM22 signature matrix at 1000 permutations, which allows for high sensitivity and specific discrimination of 22 human immune phenotypes [23, 24]. Each sample was screened by the R package “Genefilter,” and the statistical significance threshold was set to a p-value of 0.05. Then the final CIBERSORT output was analyzed.
Analysis of immune-related genes
In order to obtained immune-related genes differentially expressed between the groups, we took the intersection of the differentially expressed mRNAs and the immune genes set, downloaded from The ImmPort Shared Data (https://www.immport.org/home). In addition, we compared the expression differences of fifteen immune checkpoint molecules and twenty costimulatory molecules between the groups [25]. The threshold for significance was set as p-value < 0.05 and|log2 fold change|> 1.0.
Results
Differences in somatic mutations
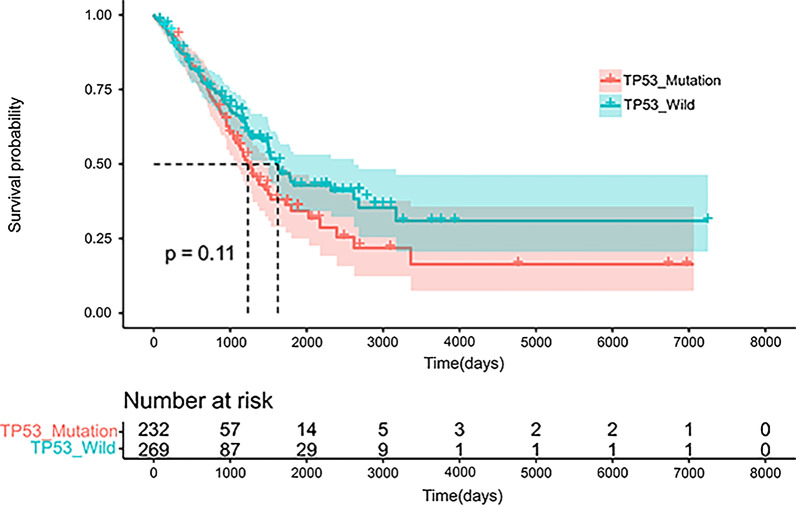
On the basis of the mutation of the TP53 gene in the sample tissues, we divided the somatic mutations data into a wild group (WT, n = 295) and a mutant group (MU, n = 265). We first analyzed the distribution of the somatic mutations between the MU and WT (Additional file 1: Figure S1). To understand the difference in clinical features between the WT (n = 274) and the MU (n = 235), we compared the age, gender, stage, and TNM stage of the two groups (Table 1). The results showed that people younger than or equal to 65 years old accounted for a higher proportion in the MU. However, no significant differences were found in other aspects, such as gender, stage and TNM stage. And no statistically significant difference in survival between the groups was observed (Fig. 1). We also analyzed the proportions of various TP53 mutation in the MU (Additional file 1: Figure S2A). The highest proportion of mutation was missense mutation, accounting for more than half (61.9%), followed by nonsense mutation (19.71%) and frame_shift_del (9.32%), while the remaining mutation types accounted for less than10%. We also found that the mutation of TP53 are mainly concentrated in the three domains of the P53 protein, including the Pro-rich domain (PRD), the central DNA binding domain (DBD), and the tetramerization domain (TD), especially the three sites (R158L/P/AFs*12, G245V/S/C, R273L/G/H/C) in the DBD (Additional file 1: Figure S2B).
Table 1.
Clinical features of the TCGA samples
| Characteristics | Mutation (N = 235) | Wild (N = 274) | p value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| Age | 0.005 | ||||
| ≤ 65 | 127 | 54.04 | 109 | 39.78 | |
| > 65 | 102 | 43.41 | 153 | 55.84 | |
| NA | 6 | 2.55 | 12 | 4.38 | |
| Sex | 0.994 | ||||
| Male | 109 | 46.38 | 127 | 46.35 | |
| Female | 126 | 53.62 | 147 | 53.65 | |
| Stage | 0.630 | ||||
| Stage I | 120 | 51.06 | 155 | 56.57 | |
| Stage II | 60 | 25.53 | 59 | 21.54 | |
| Stage III | 38 | 16.17 | 45 | 16.42 | |
| Stage IV | 14 | 5.96 | 11 | 4.01 | |
| NA | 3 | 1.28 | 4 | 1.46 | |
| T | 0.565 | ||||
| T1 | 75 | 31.91 | 93 | 33.94 | |
| T2 | 131 | 55.74 | 145 | 52.92 | |
| T3 | 19 | 8.09 | 25 | 9.12 | |
| T4 | 8 | 3.40 | 11 | 4.01 | |
| NA | 2 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| M | 0.190 | ||||
| M0 | 150 | 63.83 | 195 | 71.17 | |
| M1 | 14 | 5.96 | 11 | 4.01 | |
| NA | 71 | 30.21 | 68 | 24.82 | |
| N | 0.384 | ||||
| N0 | 146 | 62.13 | 180 | 65.69 | |
| N1 | 50 | 21.28 | 47 | 17.15 | |
| N2 | 33 | 14.04 | 40 | 14.60 | |
| N3 | 2 | 0.85 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| NA | 4 | 1.70 | 7 | 2.55 | |
Fig. 1.
Survival analysis: survival time analysis of 501 patients with TP53 status
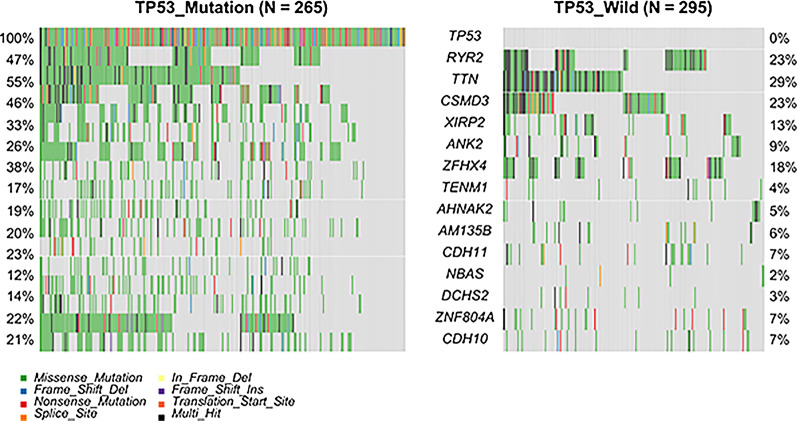
Taking FDR < 0.05 as the screening criteria, 787 significant mutations were distinguished between the MU and the WT (Fig. 2). The somatic mutation rates of titin (TTN; WT, 29% vs. MU, 55%; p < 0.001); type 2 ryanodine receptor (RYR2; WT,23% vs. MU,47%; p < 0.001); CUB and Sushi multiple domains 3(CSMD3; WT,23% vs. MU,46%; p < 0.001) and Xin-actin binding repeat containing 2(XIRP2; WT, 13% vs. MU, 33%; p < 0.001) were higher in the MU, while ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM; WT, 11.2% vs. MU, 3.8%; p = 0.011) and Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS; WT, 30.2% vs. MU, 18.5%; p = 0.012) were higher in the WT. Additionally, the mutation rate of the epidermal growth factor receptor(EGFR) was not significantly different between the groups. The somatic cell interactions function was performed to detect the correlation between the top 25 genes with different somatic mutation rates (Additional file 1: Figure S3). Except for the closely related TTN, most of the mutated genes are mutually exclusive, including the KRAS. The results strongly indicated that these mutations might be involved in the occurrence and development of LUAD.
Fig. 2.
Somatic mutation waterfall map grouped by TP53 status, the left group corresponded to the TP53 mutation group, and the right was the TP53 wild group
Differential genes expression (DEGs)
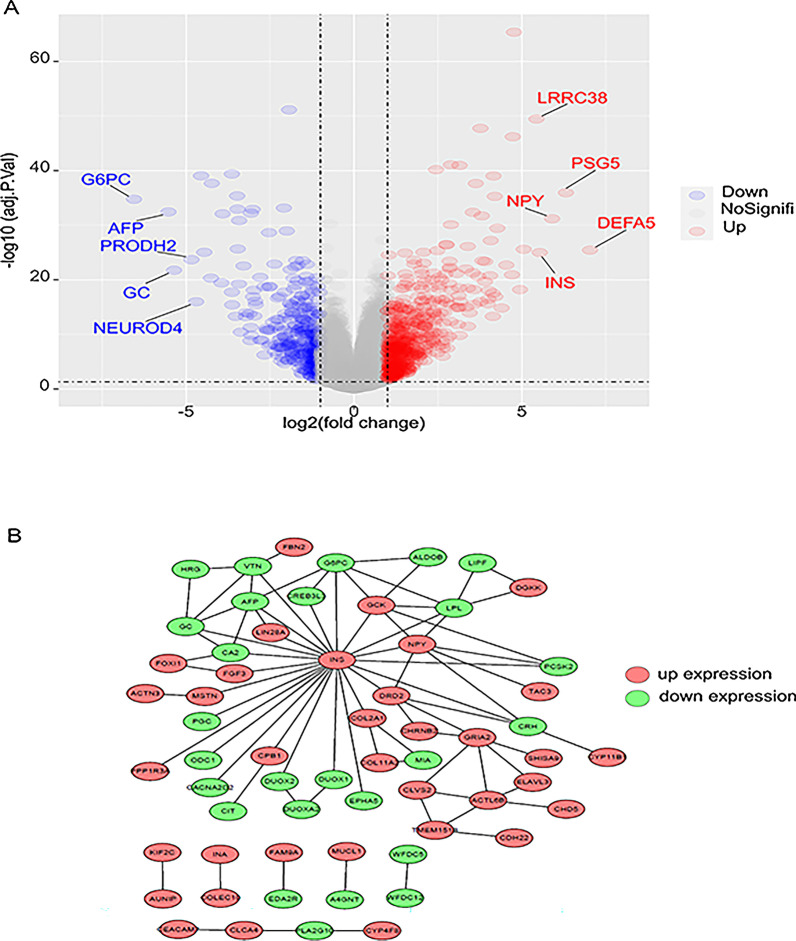
In order to study the impact of TP53 mutation on gene expression, we matched and grouped the obtained RNA-seq data with somatic mutation data, and then analyzed the differential genes expression between the MU (n = 231) and WT (n = 278). Using the WT as a standard, 542 up-regulated mRNAs and 381 down-regulated mRNAs were detected from the MU. among which alpha-defensin 5 (DEFA5) was the most significantly differentially expressed gene (logFC = 7.03, p < < 0.001) (Fig. 3A).
Fig. 3.
A Volcano map of differential gene expression from TCGA database between the groups with or without TP53 mutation. (Red represents high expression in the group with TP53 mutation, blue represents high expression in the group without TP53 mutation). B Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of differently expressed genes
To further study the relationship between DEGs, we established and analyzed the protein-protein interactions (PPIs), which was based on the top 100 DEGs. The results showed that INS, NPY(logFC = 5.90, p < < 0.001), and AFP were located in the center of the PPI map (Fig. 3B). We also constructed the transcription factor regulation network of all DEGs and found that the transcription factors CHX10, S8 and LHX3 were the hub in the network. (Additional file 1: Figure S4). These genes might be associated with the mutation of TP53 between the groups.
The correlation between miRNAs and lncRNAs with the mutation of TP53
Both miRNAs and lncRNAs play vital roles in epigenetic regulation. The differentially expressed miRNAs and IncRNAs were calculated according to the above method of analyzing mRNAs. 57 up-regulated miRNAs and 17 down-regulated miRNAs were obtained (Additional file 1: Figure S5A). MiR-371a-5p was found to be the most significant up-regulated (logFC = 7.62, p < 0.0001), while miR-122-5p was the most down-regulated (logFC = − 3.87, p < 0.0001) miRNAs. At the same time, 298 up-regulated and 200 down-regulated lncRNAs were discovered between the two groups (Additional file 1: Figure S5B). Of these IncRNAs, LINC02106 was the most substantially up-regulated (logFC = 4.70, p < 0.0001), and AC112495.1 was the most significantly down-regulated (logFC= − 4.94, p < 0.0001). Next, a ceRNA network composed of differential mRNAs, miRNAs, and lncRNAs was established. We found that DLX6-AS1 regulated most miRNAs and mRNAs (Fig. S6), which may be related to the mutation of the TP53.
Gene functional analysis
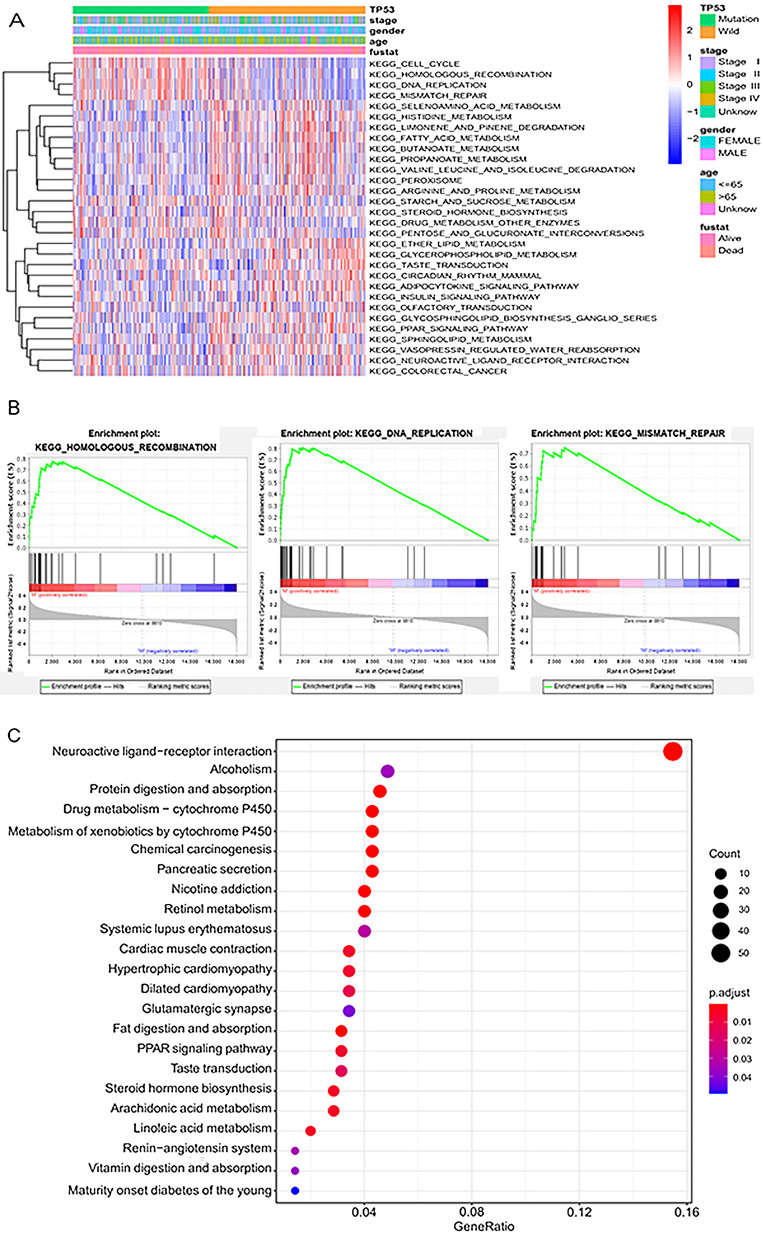
Gene set variation analysis (GSVA) is an unsupervised method of gene set enrichment, which is used to evaluate pathway activity variation in a simple population in an unsupervised manner. GSVA analysis discovered 30 different gene sets between the MU and the WT (p < 0.05). Taking the WT as a reference, the expression of 12 pathways was up-regulated in the MU, most of which were associated with cell division, such as cell cycle, homologous recombination, and DNA replication (Fig. 4A). To understand the functions of DEGs, we performed Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses enrichment analysis based on GSEA analysis. Finally, it was found that 12 pathways were enriched in the MU, most of which were associated with DNA, including homologous recombination, DNA replication, and mismatch repair. This indicates that the mutation of the TP53 gene does have a significant effect on cell division (Fig. 4B).
Fig. 4.
A Heatmap of gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA Seq data (GSVA). B The three most significant path ways of Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA). C Barplot of significantly different pathways from KEGG analysis of all aberrant genes
To characterize 923 differentially expressed mRNAs, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis was performed. The results showed that 23 pathways were enriched, and the significant pathways were closely related to metabolism (Fig. 4C).
Immune cell infiltration landscapes in the WT and MU.
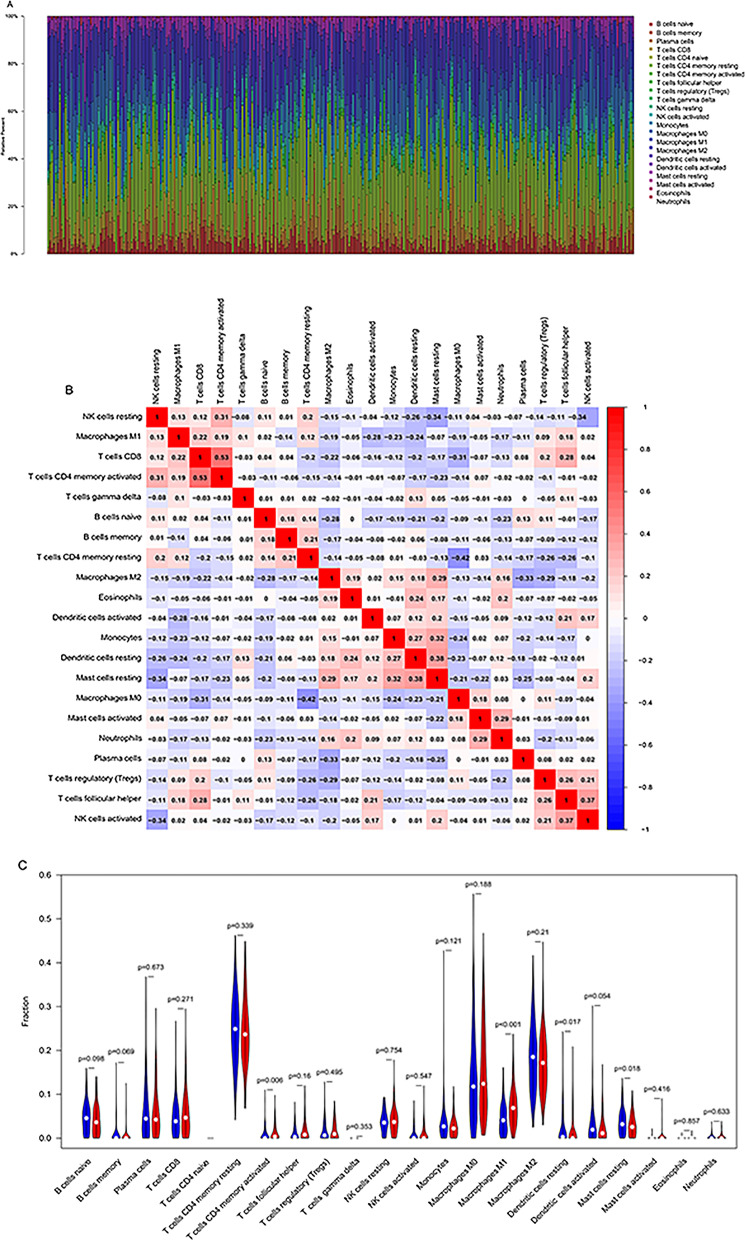
We next investigated the distinction in immune infiltration between the MU and WT. As shown in Fig. 5A, there was a significant difference in the proportion of 22 tumor immune cell types between WT and MU. Additionally, the proportion of immune cells was weak to moderately correlated (Fig. 5B). We also found that Macrophages M1 (p < 0.001), T cells CD4 memory activated (p = 0.006), Mast cells resting (p = 0.018), and Dendritic cells resting (p = 0.017) showed significant differences in expression (Fig. 5C). The distinction of immune cell infiltration between the MU and WT might offer new ideas and targets for immunotherapy, which may have a vital clinical significance.
Fig. 5.
Immune cell infiltration landscapes in patients of LUAD with or without TP53 mutation. A Relative proportions of immune cell infiltration in the wild group and mutant group. B Correlation heat map of immune cells. C Differences in immune cell infiltration abundances between wild and mutant group
Differences in immune genes.
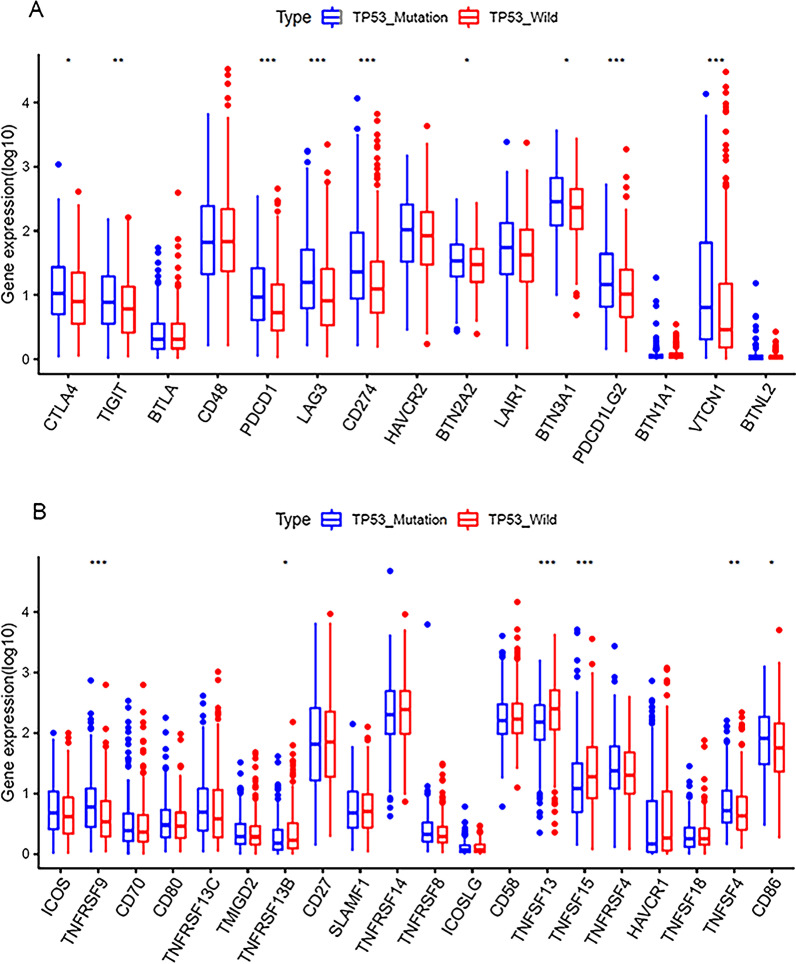
To describe the impact of TP53 gene mutation on immune-related genes, we first downloaded a list of immune-related genes from The ImmPort Shared Data, took the intersection with the previously obtained differentially expressed mRNAs, and performed the differential analysis of the obtained results, finally screened out 6 up- regulated and 29 down-regulated immune-related genes. (Additional file 1: Figure S7). VGF was the most substantially up-regulated (logFC = 1.86, p < 0.0001), and PGC was the most significantly down-regulated (logFC = - 4.19, p < 0.0001).In addition, we investigated the expression patterns of several immunomodulators between the groups, including fifteen immune checkpoint molecules (Fig. 6A) and twenty costimulatory molecules (Fig. 6B). Some highly expressed costimulating and co-inhibitory molecules in MU were observed, such as PD-1, PD-L1, TNFSF13, and TNFRSF9. This suggests that these patients may benefit from immunotherapy.
Fig. 6.
Expression of immune modulators (*represents P < 0.05, ** represents P < 0.01, ***represents P < 0.001). Relative expression level of immune co-inhibitors (A) and co-stimulators (B)
Discussion
Despite a recent decline in incidence, lung cancer remains the leading cause of death by cancer [26]. Previous studies had shown that compared with the corresponding wild-type tumors, TP53 mutant NSCLC expressed higher levels of PD-L1 protein, promoted T cell infiltration, and enhanced tumor immunogenicity [27, 28]. However, the characteristics of patients with TP53 mutation in lung adenocarcinoma are still unclear. In this study, we have first clarified the effect of TP53 mutation on the microenvironment and genetics of patients with LUAD, which will help us understand the underlying molecular mechanisms and be used clinically in the future.
The entire TTN gene consists of 364 exons, located on chromosome 2q31, and its mutation is thought to be related to a variety of skeletal muscle and cardiomyopathy [29]. In our study, we found that the mutation rate of TTN was higher in the MU. The previous research has proved that TTN and TP53 mutations may have a combined effect in LUSC, and mutation in the TTN gene show good predictive value in LUSC, but this effect does not apply to LUAD [30]. Another study indicated that the frequency of TTN mutation showed the highest correlation with the response rate to immune checkpoint blockades for individual tumor types, including LUAD [31].
We also studied the associations of mutation with clinical features and outcomes. We found that the TP53 gene had a higher mutation rate in people younger than or equal to 65 years old, reaching 53.8%, and it was only 40% in people over 65 years.
old, which was consistent with the results of previous studies [32, 33]. We also confirmed that TP53 mutation did not affect the prognosis of patients with LUAD, it was consistent with the result of the study by Szymanowska, A., et al. [34–39]. However, other studies suggested that patients with mutation of the TP53 gene had a poor prognosis [15, 32, 33, 40, 41]. This phenomenon was worth studying. In fact, only the OS of patients who received specific treatment was considered to be related to the mutation of TP53. In contrast, for patients who had not received treatment, the mutation of TP53 did not affect the prognosis. In addition, we found that there was no difference in TP53 mutation between genders; both were 47%, the same was true for Marrogi, A. J., et al. [42]
At the same time, we found that the mutation had a significant impact on gene expression, such as DEFA5 and NPY, which had higher expression in the MU. DEFA5 is an alpha-defensins [43], produced and secreted by Paneth cells [44]. It was reported that DEFA5 peptide was highly presented in cancers, including lung cancer [45]. In gastric cancer, the overexpression of DEFA5 can inhibit cell proliferation and tumor growth [46]. Similarly, in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, DEFA5 can inhibit the growth of cancer cells by down-regulating the expression of E-cadherin [47]. All these indicated that DEFA5 may have a specific tumor inhibitory effect. But further researches are needed to clarify the specific mechanisms of DEFA5 affecting LUAD. NPY gene was not only highly expressed in the MU, but also in a relatively central position in the PPI map. NPY encoded by the NPY gene is a 36 amino acid neuropeptide, which is involved in the regulation of a large number of physiological and pathophysiological processes in the cardiopulmonary system, immune system, nervous system and endocrine system [48]. Some studies have shown that high expression of NPY can affect the cell cycle and promote tumor invasion and metastasis [49, 50], also in LUAD [33].
We also studied the changes in the function of differentially expressed genes. The results showed that the effect of mutation on gene function was closely related to cell division. For instance, after GSVA analysis, we found that the cell cycle and homologous recombination were significantly up-regulated in the MU. Regulation of cell cycle is a complicated biological process, and numerous regulatory proteins, including TP53, participate in it [51]. Homologous recombination repairs DNA double-strand breaks in S-phase post -replication or G2 in a generally error-free manner [52]. A previous study showed that wild-type TP53 could inhibit replication-associated homologous recombination [53].
Significantly upregulated and downregulated miRNAs were also identified, such as miR-371a-5p (logFC = 7.62, p < < 0.001) and miR-122-5p (logFC = − 3.87, p < < 0.001). Previous studies have revealed that miR-371a-5p can affects the MAPK signaling pathway, which is closely related to cell apoptosis and lipid metabolism [54, 55]. In contrast, the overexpression of miR-371a-5p can promote the proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells [56]. Research by Yue, L. and J. Guo et al. showed that miR-371a-5p promoted the development of pancreatic cancer [57]. However, the role of miR-371a-5p in LUAD needs to be further investigated. The low expression of miR-122-5p is more common in the MU in our research. As a tumor suppressor gene [58], it plays a crucial role in inhibiting the metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of NSCLC [59]. DLX6-AS1 regulated the most differentially expressed genes. The high expression of DLX6-AS1 is related to the disease stage, positive lymph node metastasis, and poor tumor differentiation in advanced NSCLC [60]. The low expression of DLX6-AS1 can significantly inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells and induce apoptosis [61–63]. But in our study, DLX6-AS1 is highly expressed in the MU.
We have also focused on the relationship between TP53 mutation and immunity. In terms of immune genes, we found that VGF and PGC are the most apparent up-regulated and down-regulated immune genes. A study indicated that VGF significantly promotes the resistance of human lung cancer cells to EGFR kinase inhibitors and is also related to the poor survival of patients with LUAD [64]. Matsumoto, T., et al. believed that VGF is only expressed in neuroendocrine carcinoma-derived cells and can be used as a new serological diagnostic marker for pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors [65]. PGC-1α is a crucial transcription regulator of genes that control energy metabolism and mitochondrial biogenesis through its partner transcription factors: nuclear respiratory factors and PPARs [66]. Overexpression of PGC-1α enhanced the efficacy of PD-1 blockers in lung cancer [67]. Both costimulating and co-inhibitory molecules have higher expression in the MU, including PD1 and PDL1. PD1 is located on lymphocytes, and PDL1 is located on antigen presenting cells. Their interaction leads to tolerance of the immune system to tumor cells. Sun, H., et al. believed that mutant TP53 may enhance PD-L1 expression by activating the newly acquired function of BCL2L1 /JAK3/STAT1 signaling [68]. However, in several reports of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for NSCLC, the expression of PD-L1 in tumors has been considered to be a standard and predictive biomarker for poor prognosis [14, 69]. Previous studies had shown that the survival outcome of patients with various types of cancer treated by immunotherapy was significantly related to the immune cells infiltrated in the tumor [70]. In our study, we found that macrophages M1 and T cells CD4 memory activated were comparatively upregulated in the MU, while mast cells resting and dendritic cells resting were downregulated. A report indicated that mast cells could promote growth and metastasis by producing IL-1β during LUAD progression [71].
Our study also has some limitations. First, the information from the TCGA database lacks some essential clinicopathological information, such as the patient’s treatment; secondly, to verify our results, another independent cohort study and more in vitro or in vivo studies should be conducted.
Conclusions
To sum up, our study described the impact of TP53 gene mutations on the genome and microenvironment in patients with LUAD. Compared with the WT, patients in the MU with LUAD had different microenvironmental RNAs and miRNAs, including immune cell infiltration and immunomodulators. We hope that this study can deepen our understanding of the pathogenesis of TP53 mutant LUAD and provide a reference for further research.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Supplementary information.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank the researchers who provided the data to the TCGA database.
Abbreviations
- LUAD
Lung adenocarcinoma
- MU
Mutant group
- WT
Wild-type group
- TTN
Titin
- RYR2
Type 2 ryanodine receptor
- CSMD3
CUB and Sushi multiple domains 3
- DEFA5
α-defensin 5
- PSG5
Pregnancy-specific glycoprotein 5
- NPY
Neuropeptide Y
- G6PC
Glucose-6-phosphatase
- AFP
Alpha-fetoprotein
- GC
Carry gametocidal
- VGF
VGF nerve growth factor inducible
- PGC
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator
- NSCLC
Non-small cell carcinoma
- DGEs
Differentially expressed genes
- PPI
Protein–protein interactions
- GO
Gene ontology
- KEGG
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- GSEA
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
- GSVA
Gene Set Variation Analysis
- PRD
Pro-rich domain
- DBD
The central DNA binding domain
- TD
Tetramerization domain
- XIRP2
Xin-actin binding repeat containing 2
- ATM
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated
- KRAS
Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene
- EGFR
Epidermal growth factor receptor
Authors’ contributions
DJZ: Collection and assembly of data, Data analysis and interpretation, Writing – original draft. ZYH: Collection and assembly of data, Data analysis and interpretation. YJY: Collection and assembly of data, Writing – original draft. BV: Collection and assembly of data. GYS: Writing – original draft. ZCC: Data analysis and interpretation. CZ: Conception and design. ML: Conception and design, Writing -review & editing. ZWL: Conception and design, Funding acquisition, Writing - review & editing. QW: Funding acquisition, Writing - review & editing. Final approval of the manuscript: All authors.
Funding
This work was supported by the Training Programme for the Talents of Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University (Grant No. 2019ZSYXGG06).
Availability of data and materials
The data set analyzed in this study can be queried in the TCGA database ( https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/).
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable to current research.
Consent for publication
Not applicable to current research.
Competing interests
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Dejun Zeng, Zhengyang Hu and Yanjun Yi have contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Miao Lin, Email: lin.miao@zs-hoapital.sh.cn.
Zongwu Lin, Email: lin.zongwu@zs-hospital.sh.cn.
References
- 1.Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sutherland KD, Berns A. Cell of origin of lung cancer. Mol Oncol. 2010;4(5):397–403. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2010.05.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barta JA, Powell CA, Wisnivesky JP. Global epidemiology of lung cancer. Ann Glob Health 2019;85(1). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Schabath MB, Cote ML. Cancer progress and priorities: lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2019;28(10):1563–1579. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yamamoto S, Iwakuma T. Regulators of oncogenic mutant TP53 gain of function. Cancers 2019;11(1). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Vogelstein B, Lane D, Levine AJ. Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 2000;408(6810):307–310. doi: 10.1038/35042675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kruiswijk F, Labuschagne CF, Vousden KH. p53 in survival, death and metabolic health: a lifeguard with a licence to kill. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2015;16(7):393–405. doi: 10.1038/nrm4007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Oren M, Rotter V. Mutant p53 Gain-of-function in cancer. Csh Perspect Biol. 2010;2(2). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 9.Olivier M, Hollstein M, Hainaut P. TP53 mutations in human cancers: origins, consequences, and clinical use. Csh Perspect Biol. 2010;2(1). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Hainaut P, Pfeifer GP. Somatic TP53 mutations in the era of genome sequencing. Csh Perspect Med . 2016;6(11). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Baugh EH, Ke H, Levine AJ, Bonneau RA, Chan CS. Why are there hotspot mutations in the TP53 gene in human cancers? Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(1):154–160. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mogi A, Kuwano H. TP53 mutations in nonsmall cell lung cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 13.Morton JP, Timpson P, Karim SA, Ridgway RA, Athineos D, Doyle B, Jamieson NB, Oien KA, Lowy AM, Brunton VG, et al. Mutant p53 drives metastasis and overcomes growth arrest/senescence in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(1):246–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908428107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wu C, Rao X, Lin W. Immune landscape and a promising immune prognostic model associated with TP53 in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 2021;10(3):806–823. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhao L, Qu X, Wu Z, Li Y, Zhang X, Guo W. TP53 somatic mutations are associated with poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer patients who undergo immunotherapy. Aging (Albany NY) 2020;12(14):14556–14568. doi: 10.18632/aging.103502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Scoccianti C, Vesin A, Martel G, Olivier M, Brambilla E, Timsit JF, Tavecchio L, Brambilla C, Field JK, Hainaut P, et al. Prognostic value of TP53, KRAS and EGFR mutations in nonsmall cell lung cancer: the EUELC cohort. Eur Respir J. 2012;40(1):177–184. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00097311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mayakonda A, Lin DC, Assenov Y, Plass C, Koeffler HP. Maftools: efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 2018;28(11):1747–1756. doi: 10.1101/gr.239244.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sui Q, Liang J, Hu Z, Chen Z, Bi G, Huang Y, Li M, Zhan C, Lin Z, Wang Q. Genetic and microenvironmental differences in non-smoking lung adenocarcinoma patients compared with smoking patients. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020;9(4):1407–1421. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(1):139–140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hu ZY, Bi GS, Sui QH, Bian YY, Du YJ, Liang JQ, Li M, Zhan C, Lin ZW, Wang Q. Analyses of multi-omics differences between patients with high and low PD1/PDL1 expression in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;88. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 21.Yu GC, Wang LG, Han YY, He QY. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics. 2012;16(5):284–287. doi: 10.1089/omi.2011.0118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hanzelmann S, Castelo R, Guinney J. GSVA: gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14:7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chen B, Khodadoust MS, Liu CL, Newman AM, Alizadeh AA. Profiling tumor infiltrating immune cells with CIBERSORT. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1711:243–259. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7493-1_12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhou R, Zhang JW, Zeng DQ, Sun HY, Rong XX, Shi M, Bin JP, Liao YL, Liao WJ. Immune cell infiltration as a biomarker for the diagnosis and prognosis of stage I-III colon cancer. Cancer Immunol Immun. 2019;68(3):433–442. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2289-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bi G, Chen Z, Yang X, Liang J, Hu Z, Bian Y, Sui Q, Li R, Zhan C, Fan H. Identification and validation of tumor environment phenotypes in lung adenocarcinoma by integrative genome-scale analysis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020;69(7):1293–1305. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02546-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bade BC, Dela Cruz CS. Lung Cancer 2020 epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med. 2020;41(1):1-+. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2019.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dong ZY, Zhong WZ, Zhang XC, Su J, Xie Z, Liu SY, Tu HY, Chen HJ, Sun YL, Zhou Q, et al. Potential predictive value of TP53 and KRAS mutation status for response to PD-1 blockade immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(12):3012–3024. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cortez MA, Ivan C, Valdecanas D, Wang X, Peltier HJ, Ye Y, Araujo L, Carbone DP, Shilo K, Giri DK, et al. PDL1 regulation by p53 via miR-34. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2016;108(1). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Kellermayer D, Smith JE, Granzier H. Titin mutations and muscle disease. Pflugers Arch. 2019;471(5):673–682. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02272-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cheng X, Yin H, Fu J, Chen C, An J, Guan J, Duan R, Li H, Shen H. Aggregate analysis based on TCGA: TTN missense mutation correlates with favorable prognosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019;145(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-02861-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jia Q, Wang J, He N, He J, Zhu B. Titin mutation associated with responsiveness to checkpoint blockades in solid tumors. JCI Insight. 2019;4(10). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Li XM, Li WF, Lin JT, Yan HH, Tu HY, Chen HJ, Wang BC, Wang Z, Zhou Q, Zhang XC, et al. Predictive and prognostic potential of TP53 in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated with EGFR-TKI: analysis of a phase III randomized clinical trial (CTONG 0901) Clin Lung Cancer. 2021;22(2):100–109. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2020.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang F, Zhao N, Gao G, Deng HB, Wang ZH, Deng LL, Yang Y, Lu C. Prognostic value of TP53 co-mutation status combined with EGFR mutation in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020;146(11):2851–2859. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Szymanowska A, Jassem E, Dziadziuszko R, Skrzypski M, Kobierska-Gulida G, Holm K, Borg A, Rzyman W, Limon J, Jassem J. [Analysis of prognostic value of TP53 gene mutations in non-small cell lung cancer] Pneumonol Alergol Pol. 2005;73(3):264–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Liu DH, Zhao ZR, Lin YB, Zhou WJ, Hou JY, Ye ZH, Long H. Prognostic effect of TP53 and PKD co-mutations in patients with resected epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019;26(6):1934–1941. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liu Y, Xu F, Wang Y, Wu Q, Wang B, Yao Y, Zhang Y, Han-Zhang H, Ye J, Zhang L, et al. Mutations in exon 8 of TP53 are associated with shorter survival in patients with advanced lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(3):3159–3169. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hou Y, Tan S, Wang G. Significance of TP53 mutation in cellular process and disease progression in lung adenocarcinoma. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2021. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 38.Frost N, Kollmeier J, Vollbrecht C, Grah C, Matthes B, Pultermann D, von Laffert M, Luders H, Olive E, Raspe M, et al. KRAS(G12C)/TP53 co-mutations identify long-term responders to first line palliative treatment with pembrolizumab monotherapy in PD-L1 high (>/=50 %) lung adenocarcinoma. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021;10(2):737–752. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Canale M, Petracci E, Delmonte A, Bronte G, Chiadini E, Ludovini V, Dubini A, Papi M, Baglivo S, De Luigi N , et al. Concomitant TP53 mutation confers worse prognosis in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with TKIs. J Clin Med. 2020;9(4). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 40.Freudenstein D, Litchfield C, Caramia F, Wright G, Solomon BJ, Ball D, Keam SP, Neeson P, Haupt Y, Haupt S. TP53 status, patient sex, and the immune response as determinants of lung cancer patient survival. Cancers (Basel). 2020;12(6). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 41.Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Onozato R, Kuwano H, Mitsudomi T. Prognostic implication of EGFR, KRAS, and TP53 gene mutations in a large cohort of Japanese patients with surgically treated lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4(1):22–29. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181914111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Marrogi AJ, Mechanic LE, Welsh JA, Bowman ED, Khan MA, Enewold L, Shields PG, Harris CC. TP53 mutation spectrum in lung cancer is not different in women and men. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14(4):1031–1033. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lehrer RI, Lu W. alpha-Defensins in human innate immunity. Immunol Rev. 2012;245(1):84–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01082.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Bevins CL, Salzman NH. Paneth cells, antimicrobial peptides and maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9(5):356–368. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Droin N, Hendra JB, Ducoroy P, Solary E. Human defensins as cancer biomarkers and antitumour molecules. J Proteomics. 2009;72(6):918–927. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2009.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wu ZW, Ding ZH, Cheng B, Cui ZC. The inhibitory effect of human DEFA5 in growth of gastric cancer by targeting BMI1. Cancer Sci. 2021;112(3):1075–1083. doi: 10.1111/cas.14827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nomura Y, Tanabe H, Moriichi K, Igawa S, Ando K, Ueno N, Kashima S, Tominaga M, Goto T, Inaba Y, et al. Reduction of E-cadherin by human defensin-5 in esophageal squamous cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;439(1):71–77. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Groneberg DA, Folkerts G, Peiser C, Chung KF, Fischer A. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2004;17(4):173–180. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2004.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ulum B, Mammadova A, Ozyuncu O, Uckan-Cetinkaya D, Yanik T, Aerts-Kaya F. Neuropeptide Y is involved in the regulation of quiescence of hematopoietic stem cells. Neuropeptides 2020;80. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 50.Hong SH, Tilan JU, Galli S, Izycka-Swieszewska E, Polk T, Horton M, Mahajan A, Christian D, Jenkins S, Acree R, et al. High neuropeptide Y release associates with Ewing sarcoma bone dissemination - in vivo model of site-specific metastases. Oncotarget. 2015;6(9):7151–7165. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schafer KA. The cell cycle: a review. Vet Pathol. 1998;35(6):461–478. doi: 10.1177/030098589803500601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sirbu BM, Lachmayer SJ, Wulfing V, Marten LM, Clarkson KE, Lee LW, Gheorghiu L, Zou L, Powell SN, Dahm-Daphi J, et al. ATR-p53 restricts homologous recombination in response to replicative stress but does not limit DNA interstrand crosslink repair in lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Janz C, Wiesmuller L. Wild-type p53 inhibits replication-associated homologous recombination. Oncogene. 2002;21(38):5929–5933. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zou P, Luo L, Zhao C, Chen Z, Dong R, Li N, Wang Y, Wang J, Wang T, Chen M, et al. The serum microRNA profile of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: identification of novel noninvasive biomarkers. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(3):1480–1488. doi: 10.1159/000495595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhang X, Wen L, Chen S, Zhang J, Ma Y, Hu J, Yue T, Wang J, Zhu J, Bu D et al. The novel long noncoding RNA CRART16 confers cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer cells by enhancing ERBB3 expression via miR-371a-5p. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 56.Bai PS, Hou P, Kong Y. Hepatitis B virus promotes proliferation and metastasis in male Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma patients through the LEF-1/miR-371a-5p/SRCIN1/pleiotrophin/Slug pathway. Exp Cell Res. 2018;370(1):174–188. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Yue L, Guo J. LncRNA TUSC7 suppresses pancreatic carcinoma progression by modulating miR-371a-5p expression. J Cell Physiol. 2019. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 58.Li C, Qin F, Hu F, Xu H, Sun G, Han G, Wang T, Guo M. Characterization and selective incorporation of small non-coding RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer extracellular vesicles. Cell Biosci. 2018;8:2. doi: 10.1186/s13578-018-0202-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Qin H, Sha J, Jiang C, Gao X, Qu L, Yan H, Xu T, Jiang Q, Gao H. miR-122 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2015;8:3175–3184. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S91696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang X, Guo H, Bao Y, Yu H, Xie D, Wang X. Exosomal long non-coding RNA DLX6-AS1 as a potential diagnostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;18(5):5197–5204. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Huang Y, Ni R, Wang J, Liu Y. Knockdown of lncRNA DLX6-AS1 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion while promotes apoptosis by downregulating PRR11 expression and upregulating miR-144 in non-small cell lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1851–1859. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sun W, Zhang L, Yan R, Yang Y, Meng X. LncRNA DLX6-AS1 promotes the proliferation, invasion, and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting the miR-27b-3p/GSPT1 axis. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:3945–3954. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S196865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Li J, Li P, Zhao W, Yang R, Chen S, Bai Y, Dun S, Chen X, Du Y, Wang Y, et al. Expression of long non-coding RNA DLX6-AS1 in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15:48. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0201-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hwang W, Chiu YF, Kuo MH, Lee KL, Lee AC, Yu CC, Chang JL, Huang WC, Hsiao SH, Lin SE, et al. Expression of neuroendocrine factor VGF in lung cancer cells confers resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors and triggers epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2017;77(11):3013–3026. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Matsumoto T, Kawashima Y, Nagashio R, Kageyama T, Kodera Y, Jiang SX, Okayasu I, Kameya T, Sato Y. A new possible lung cancer marker: VGF detection from the conditioned medium of pulmonary large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma-derived cells using secretome analysis. Int J Biol Marker. 2009;24(4):282–285. doi: 10.1177/172460080902400411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wan H, Xu B, Zhu N, Ren BZ. PGC-1 alpha activator-induced fatty acid oxidation in tumor-infiltrating CTLs enhances effects of PD-1 blockade therapy in lung cancer. Tumori J. 2020;106(1):55–63. doi: 10.1177/0300891619868287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bengsch B, Johnson AL, Kurachi M, Odorizzi PM, Pauken KE, Attanasio J, Stelekati E, McLane LM, Paley MA, Delgoffe GM, et al. Bioenergetic insufficiencies due to metabolic alterations regulated by the inhibitory receptor PD-1 are an early driver of CD8(+) T cell exhaustion. Immunity. 2016;45(2):358–373. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sun H, Liu SY, Zhou JY, Xu JT, Zhang HK, Yan HH, Huan JJ, Dai PP, Xu CR, Su J, et al. Specific TP53 subtype as biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma. Ebiomedicine. 2020;60:102990. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liang J, Li M, Sui Q, Hu Z, Bian Y, Huang Y, Zhan C, Jiang W, Wang Q, Tan L. Compare the efficacy and safety of programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) and programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a Bayesian analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2020;9(4):1302–1323. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-20-192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Gentles AJ, Newman AM, Liu CL, Bratman SV, Feng W, Kim D, Nair VS, Xu Y, Khuong A, Hoang CD, et al. The prognostic landscape of genes and infiltrating immune cells across human cancers. Nat Med. 2015;21(8):938–945. doi: 10.1038/nm.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Baram D, Vaday GG, Salamon P, Drucker I, Hershkoviz R, Mekori YA. Human mast cells release metalloproteinase-9 on contact with activated T cells: juxtacrine regulation by TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 2001;167(7):4008–4016. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.7.4008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Supplementary information.
Data Availability Statement
The data set analyzed in this study can be queried in the TCGA database ( https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/).