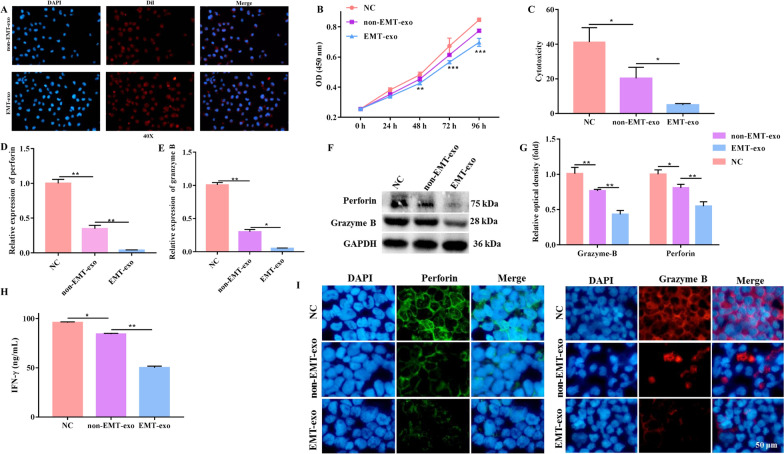
Fig. 2.
EMT-exo inhibited the function of NK92-MI cells. A Representative fluorescence microscopy image of the Dil-labeled exosomes (red) internalized by NK92-MI cells. B The viability of NK92-MI cells was detected by the CCK-8 assay. C The cytotoxicity of NK92-MI cells (pretreated with EMT-exo or not) co-cultured with SW480 cells was detected by the LDH assay. The expression of the toxic molecules perforin and granzyme B in NK92-MI cells (pretreated with EMT-exo or not) co-cultured with SW480 cells was measured by qRT-PCR (D, E) and western blotting (F, G). H The production of IFN-γ from NK92-MI cells (pretreated with EMT-exo or not) co-cultured with SW480 cells was detected by ELISA. I The expression of the toxic molecules perforin and granzyme B in NK92-MI cells was measured by immunofluorescence. GAPDH was used to normalize gene expression. The data were analyzed by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01