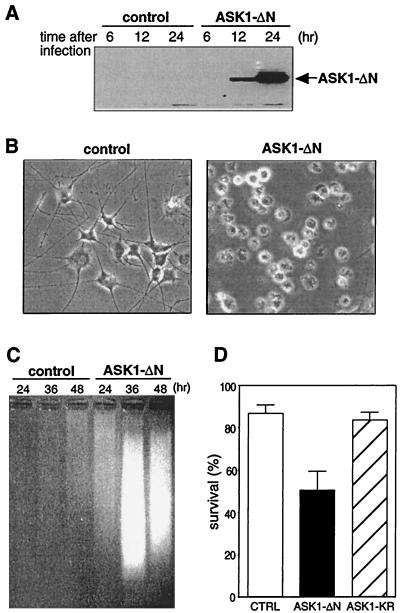
FIG. 1.
Effect of constitutively active ASK1 on neuronal survival. (A) Expression of ASK1-ΔN in PC12 cells by using recombinant adenoviruses. NGF-differentiated PC12 cells were infected with 100 PFU of recombinant adenoviruses encoding β-gal or HA-tagged ASK1-ΔN per cell. At the indicated times after infection, the cells were lysed and immunoblotted with a monoclonal antibody to HA. (B) Induction of neuronal cell death by ASK1-ΔN in NGF-differentiated PC12 cells. The morphology of β-gal-infected cells (left) and ASK1-ΔN-infected cells (right) was examined by phase-contrast microscopy 48 h after infection in the presence of 50 ng of NGF per ml. Original magnification, ×82.5. (C) DNA fragmentation in ASK1-ΔN-infected cells. Soluble cytoplasmic DNA was extracted from 3 × 106 cells after infection with recombinant adenoviruses encoding β-gal or ASK1-ΔN and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (D) Induction of neuronal cell death by ASK1-ΔN in SCG neurons. SCG neurons, cultured for 5 to 7 days in the presence of NGF, were microinjected with 0.3 mg of ASK1-ΔN (solid box), ASK1-KR (hatched box), or an empty expression vector (empty box) per ml. The 70-kDa Texas Red-dextran was included to mark the injected cells. The number of injected cells was scored 4 to 18 h after injection to allow expression of the proteins of interest (100% value). At 48 h later, the percentage of surviving cells was assessed as described in Materials and Methods. In each experiment, 200 cells were injected. The results are the means of three independent experiments and standard error of the mean.