Figure 4.
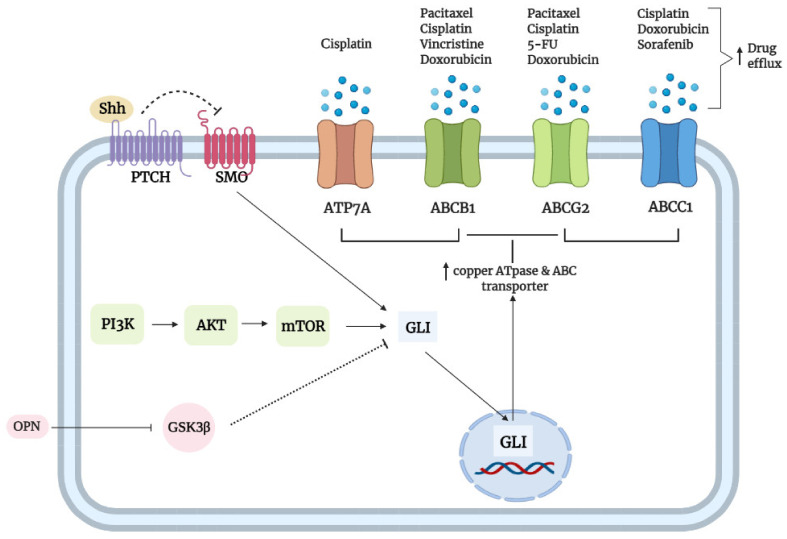
A simplified representation of canonical and noncanonical regulation of GLI in promoting transporter-mediated drug efflux. In the canonical axis, Shh binds to PTCH1, resulting in the alleviation of SMO repression and subsequent GLI activation. In the noncanonical axis, OPN inhibits the negative regulator of GLI, GSK3β, alleviating the repression of GLI1 function. Activated GLI then translocates into the nucleus, inducing the transcriptional upregulation of copper ATPase and ABC transporters to enhance drug efflux and, consequently, reduce intracellular drug levels.