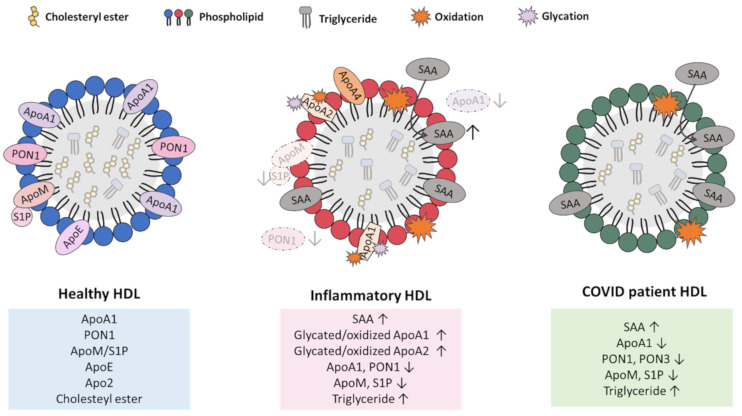
Figure 4.
HDL remodeling in inflammatory/cardiometabolic disease and COVID-19. HDL is extensively remodeled during inflammatory and cardiometabolic disease (center) and in COVID-19 patients (right). Healthy HDL is shown on the left. Similar changes in HDL in inflammatory and cardiometabolic disease include oxidation and glycation of HDL-associated proteins, including ApoA1; replacement of ApoA1 with serum amyloid A-1 (SAA1); reductions in paraoxonase 1 (PON1), ApoM/sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), and ApoE; and increases in core triglycerides. These changes are associated with reductions in the beneficial functions of HDL (anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cytotoxic properties, as well as cholesterol efflux) and gain of detrimental functions (pro-oxidant, pro-inflammatory, and pro-cytotoxic properties). Similar changes were reported in HDL during COVID-19 disease, suggesting similar changes in HDL particle functions may contribute to disease development. Arrows pointing up represents increase and arrows pointing down represents decrease for respective compound.