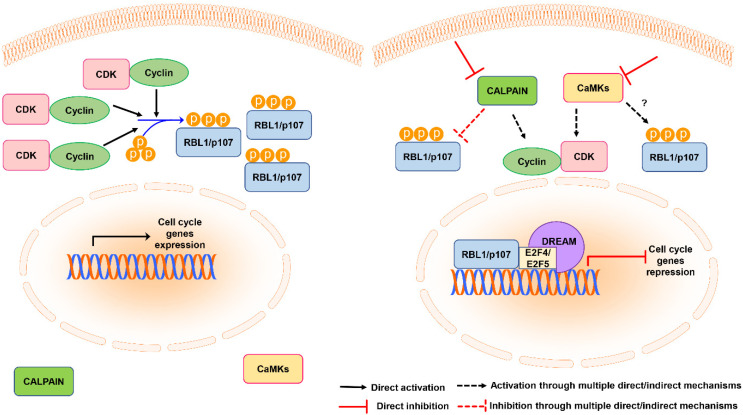
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of the model of RBL1/p107 regulation by calpain and CaMKs. In cycling cells RBL1/p107 is phosphorylated by cyclin-CDK complexes, promoting RBL1/p107 cytoplasmic localization (left panel). Calpain inhibition or CaMK inhibition promote RBL1/p107 dephosphorylation and nuclear accumulation by directly or indirectly affecting its stability or the activity/levels of cyclins and CDKs. RBL1/p107 nuclear accumulation might increase the localization of transcriptional repressors at the promoters of genes controlling cell cycle progression, contributing to cell cycle arrest (right panel).