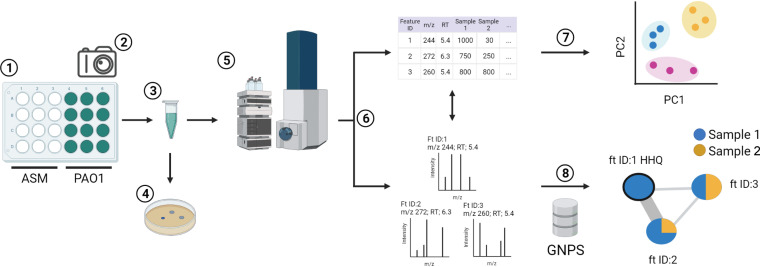
FIG 2.
Experimental workflow. (1) P. aeruginosa PAO1 growth and secondary metabolite production in artificial sputum media (ASM) was evaluated in 24-well plates (12 control wells and 12 growth wells per medium). The media were inoculated in the following three batches: batch 1, LB, Soothill, SDSU, and Cordwell ASM; batch 2, LB, Romling, Winstanley, ASMDM, and SCFM1 ASM; and batch 3, LB, SCFM2, and SCFM3 ASM. All plates were covered and incubated statically at 37°C for 72 h. (2) Growth and control wells were photographed. (3) Samples from each batch were mechanically disrupted and aliquoted. (4) A subset of aliquots (n = 3) was used to measure growth (CFU per milliliter) and culture pH. (5) Aliquots of control and growth samples (n = 12) were chemically extracted for metabolomics analysis and subjected to liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). (6) Metabolomics data from growth samples were processed for feature-based molecular networking (FBMN) using MZmine 2.0. This data processing yielded two complementary summary files, a feature quantification table and MS/MS spectral summary. The feature quantification table provided molecular ion abundance across all samples. The MS/MS spectral summary provided a representative MS/MS spectrum for each molecular ion in the feature quantification table and was used to determine compound identity using molecular networking. (7) MetaboAnalyst v5.0 was used to analyze the feature quantification table using statistical methods. (8) The MS/MS spectral summary was analyzed via the Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking (GNPS) online data analysis platform using the FBMN workflow to organize structurally related features into molecular families using MS/MS spectral similarity as a proxy for structural similarity. Spectral similarity was also used to annotate features as metabolites based on matches to the GNPS spectral libraries. Abundance data from the feature quantification table was overlaid onto the molecular network as pie charts to visually compare the relative amount of each feature present in samples from each ASM formulation.