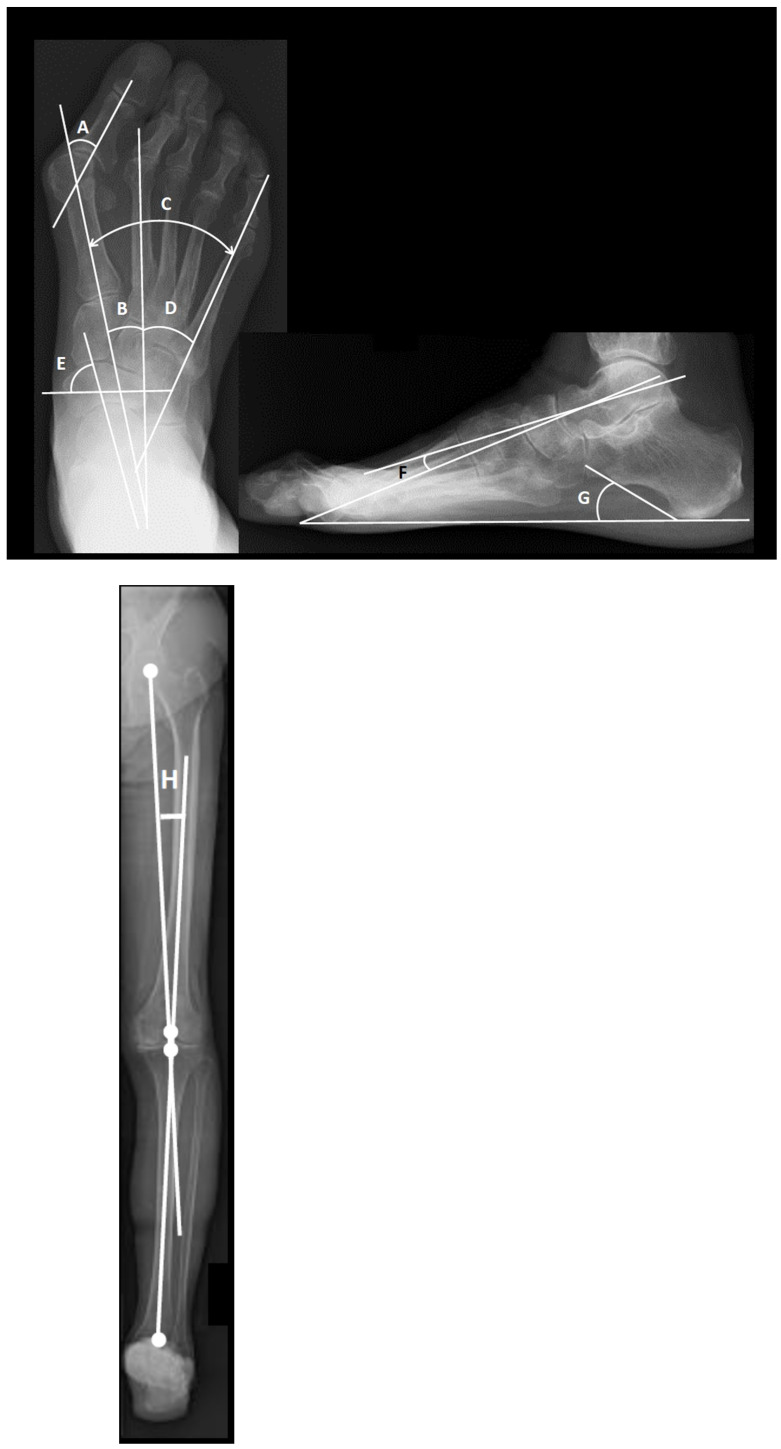
Figure 1.
Radiograph to measure parameters of foot deformity. (A) Hallux valgus (HV) angle. (B) Intermetatarsal angle between the first and second metatarsal bones (M1-M2A). (C) Intermetatarsal angle between the first and fifth metatarsal bones (M1-M5A). (D) Intermetatarsal angle between the second and fifth metatarsal bones (M2-M5A). (E) Pronated foot index (PFI: angle). The PFI is measured as the angle between the short axis of the navicular bone and the long axis of the talus bone (normal ≥65°). (F) The talo-1st metatarsal angle (Meary’s angle). (G) Calcaneal pitch angle. Radiographs taken in the weight-bearing position. (H) Hip–Knee–Ankle angle: Angle between the mechanical axis of the femur and the tibia. The mechanical axis of the femur is the line drawn from the center of the femoral head to the center of the intercondylar notch, whereas the mechanical axis of the tibia is the line connecting the center of the talus to the midpoint of the medial and lateral tibial spine tips.