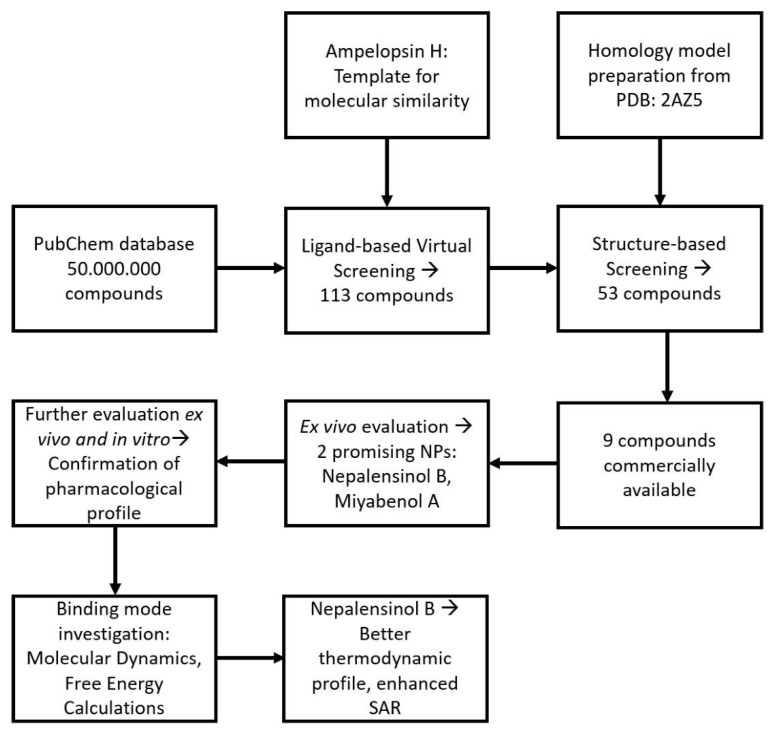
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the experimental workflow, containing a combination of pharmacological studies with computational models. The workflow starts by applying a molecular similarity search in PubChem, which yields 113 compounds. These compounds are further refined via a docking process in a homology model based on PDB: 2AZ5 (TNF dimer complex with ligand SPD304), resulting in 53 candidate ligands with a prospective affinity. Out of these compounds, 9 were commercially available, and thus they were acquired and further tested. An initial ex vivo screening in L929 cells verified that 2 compounds exhibit promising potency. Their optimal pharmacological profile was affirmed by further ex vivo testing in primary murine joints’ SFs and in vitro testing, evaluating the potential of the compounds to interrupt TNF binding to its main receptor, TNFR1. To investigate the compounds’ binding mode, a set of molecular dynamics simulations and free energy calculations was performed, suggesting that one of the two compounds, Nepalensinol B, could better serve as a candidate lead structure for anti-TNF drug design.