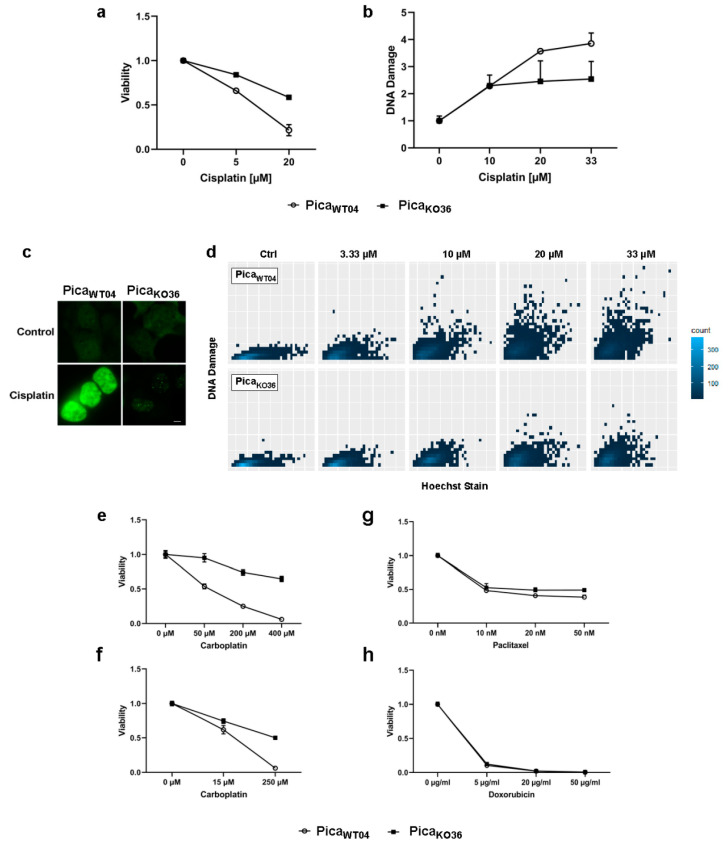
Figure 3.
VRAC expression in HNSCC cancer cells is critical for platinum drug sensitivity and specificity. (a) VRAC-deficient PicaKO36 cells are dose-dependent resistant against cisplatin. Cells were treated for 48 h, and viability was normalized to untreated controls. (b–d) Resistant VRAC-deficient cells show lower number of cisplatin-induced DNA damage events (assayed as γH2AX damage foci) per cell. Cells were treated for 24 h and γH2AX foci detected by specific antibodies. (b) DNA damage automatically quantified by high-throughput microscopy and normalized to untreated controls. (c) Fluorescence microscopy to visualize DNA damage. DNA damage (γH2AX foci) stained by specific fluorescent antibodies (green). Scale bar, 5 µm. (d) Single-cell γH2AX foci were quantified via automatic high content screening microscope Array Scan VTI and plotted via ggplot2/R [32]. (e,f), VRAC-deficient PicaKO36 2D cells (e) and 3D-tumor spheroids (f) are resistant against carboplatin treatment. Cells/spheroids were treated for 48/72 h and viability was normalized to untreated controls. (g,h) VRAC deficiency mediates cisplatin resistance but does not affect response to other cell-damaging drugs, such as paclitaxel or doxorubicin. Cells were treated for 48 h and viability was normalized to untreated controls.