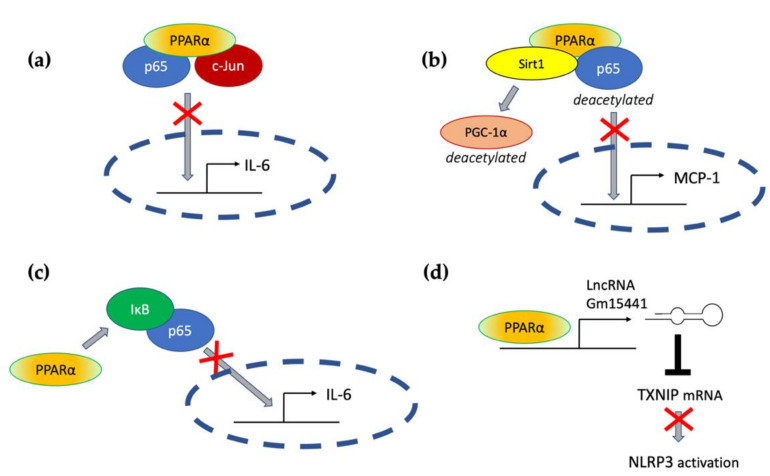
Figure 2.
The molecular mechanisms responsible for PPARα-mediated suppression of proinflammatory signaling pathways (see the main text for explanation) (a) through a direct interaction with p65 and c-Jun, (b) through interaction with Sirt1 and subsequent deacetylation of p65, (c) through activation of IκB, and (d) through transactivation of long noncoding RNA Gm15441, which interferes with the stability of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) mRNA and blocks NLRP3 inflammasome activation.