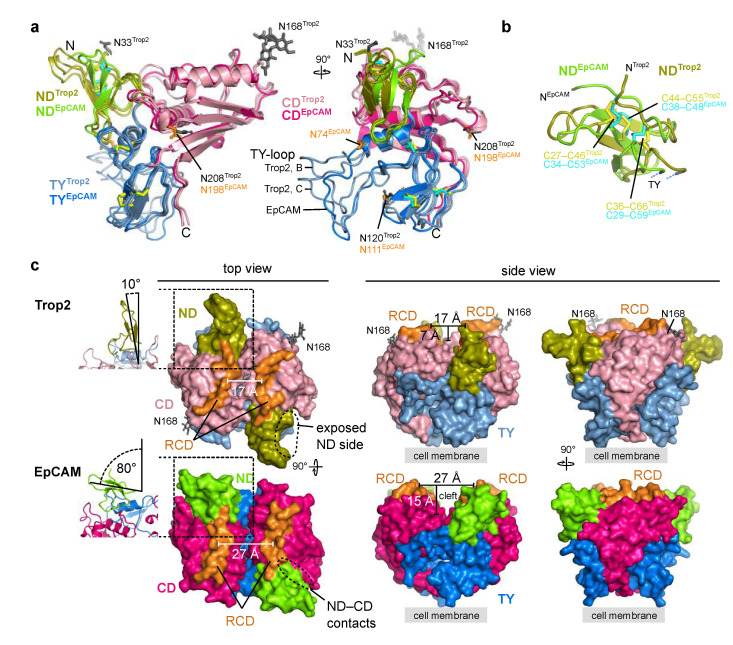
Figure 5.
Comparison of Trop2 and EpCAM ectodomain subunit structures and dimers. As EpCAM structure PDB ID 4MZV was used [6]. Trop2 domain color-coding is the same as in Figure 3, and ND, TY and CD domains of EpCAM are shown as chartreuse, marine blue and dark pink, respectively. RCD region (H227–Q239 in EpCAM, Q237–R247 in Trop2) is shown in orange. (a) Superposition of two chains of Trop2 ectodomain (chains B and C) with EpCAM ectodomain structure (PDB ID 4MZV) shown in two orientations depicts different conformations of the TY-loop. Disulfide bridges are shown as sticks (yellow for Trop2, cyan for EpCAM). (b) Superposition of ND of Trop2 (olive) and EpCAM (chartreuse) shows conserved pattern of three closely located disulfide bridges (color-coded the same as in (a)). (c) Surface representation of Trop2 and EpCAM ectodomain dimer in three different orientations demonstrates significant difference in relative orientation of the ND, different position of the RCD and a much narrower cleft in the membrane-distal region of Trop2 as compared to EpCAM. Relative orientation of the ND was defined as the angle between β-sheet of the ND and the dimer interface plain (left, ribbon representation of the region marked by rectangle). Cleft width was defined as the length of the vector (parallel to the membrane) between central parts of the juxtaposed RCDs, and cleft depth as the length of the vector (perpendicular to the membrane) between the most membrane-distal part of the dimer and the touching point of the subunits in the middle part of the dimer.