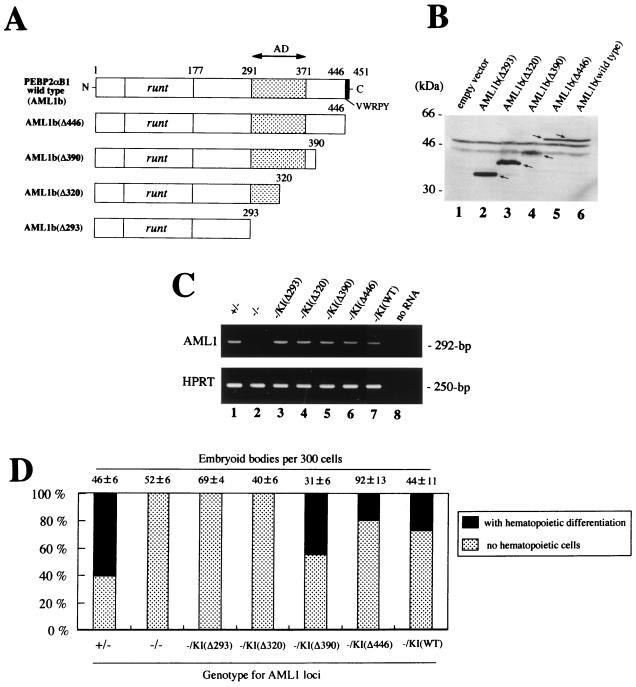
FIG. 5.
Biological properties of the C-terminal deletion mutants of AML1b. (A) Schematic representation of the module structure according to Kanno et al. (14) of the wild-type PEBP2αB1 (AML1b) and each mutant analyzed. (B) The integrity of the mutant constructs was confirmed by Western blot analysis of transiently transfected COS-7 cells. (C) Expression of the exogenous genes in ES cells were confirmed by RT-PCR analysis with primers from exons 3 and 4 (see the legend for Fig. 1D). (D) Hematopoietic differentiation of AML1−/− ES knock-in clones expressing the different AML1b mutants in a representative experiment. Dark bars indicate the percentage of the EBs with visible hematopoietic cells whereas light bars represent those without a hematopoietic element. Actual numbers of the EBs grown per 300 ES cells are given above each bar as the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate cultures.