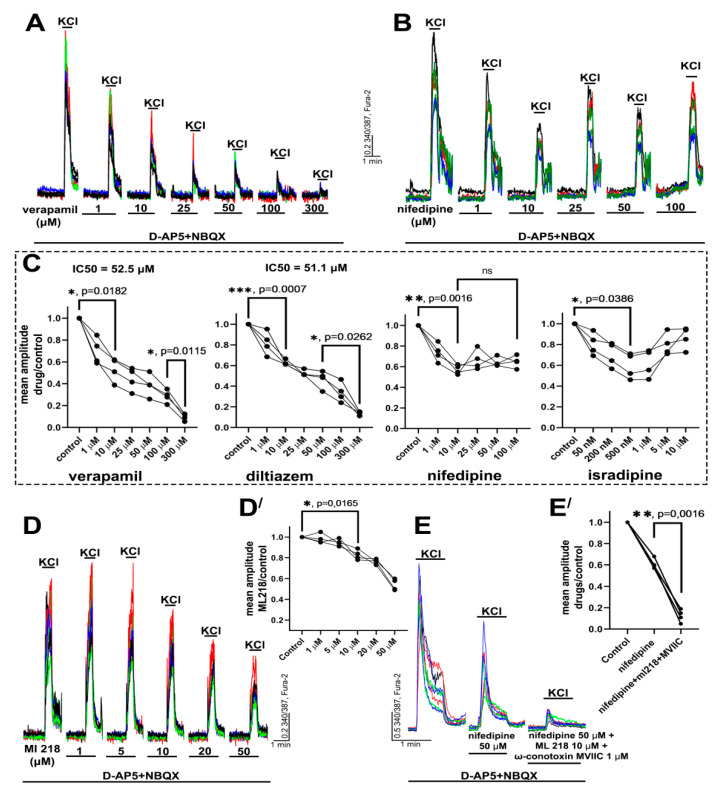
Figure 1.
The effects of different VGCC blockers on KCl-induced Ca2+ response in neurons. (A,B,D) Effects of different doses of verapamil, nifedipine, and ML-218 (T-type VGCC blocker) on the amplitude of KCl-induced (35 mM) Ca2+ response in the presence of NMDAR (D-AP5, 10 μM) and AMPAR/KAR (NBQX, 10 μM) antagonists. The pauses between KCl applications were 15 min. The traces of some representative neurons are shown in each panel. N = 100, n = 4 for each experiment. (C,D′) Diagrams showing dose-dependent changes in the mean amplitude ratio in the presence of the blocker to mean amplitude in control. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Insignificant changes are marked as n/s; p < 0.05 (*), p < 0.01 (**), p < 0.001 (***). (E,E′) Traces of neurons (E) and diagram (E′) demonstrating changes in the ratio of mean amplitude in control to mean amplitude in the presence of nifedipine, ML-218, ω-conotoxin MVIIC (blocker of P/Q- and N-type VGCC). N = 100, n = 4. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. p < 0.01 (**).