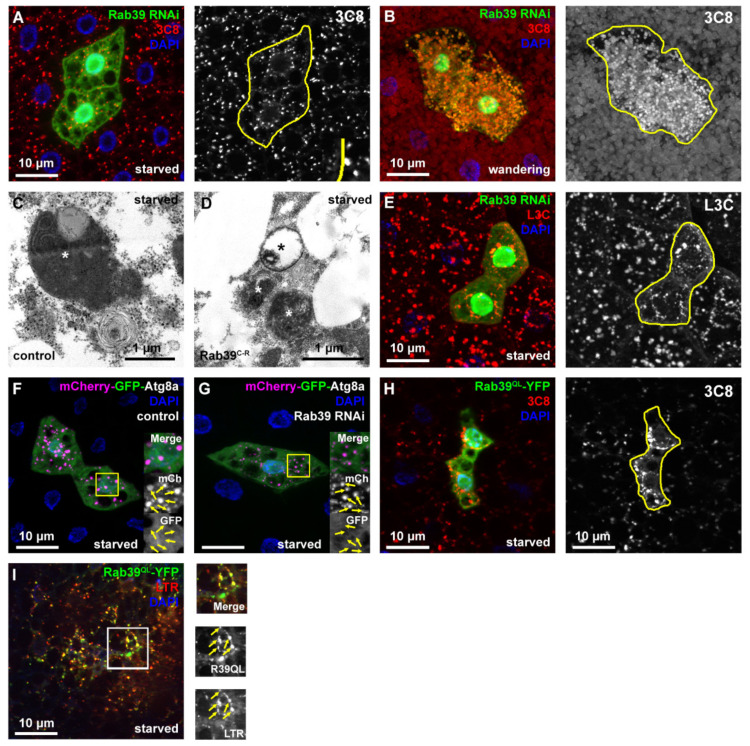
Figure 4.
Rab39 accelerates autophagic degradation in fat cells. (A,B) 3xmCherry-Atg8a was expressed in all fat cells in starved (A) or wandering (B) L3 stage animals. In the GFP-positive cells, Rab39 was silenced with RNAi (marked with yellow line in the grayscale panels). In both cases, 3xmCherry-Atg8a dots were smaller in the GFP-positive cells compared to the adjacent control cells. (A) An inset shows the size difference of 3xmCherry-Atg8 dots. (C,D) Representative electron micrographs of autolysosomes (marked with asterisks) from control (C) and Rab39 mutant (D) starved fat cells of L3 stage wandering larvae. The mutant cells contain smaller yet degrading, functional autolysosomes (i.e., no intact organelles are visible within the autolysosome), and also no autophagosome accumulation is observed. (E) dLAMP-3xmCherry expressing fat body tissue from starved L3 stage larvae: Rab39 RNAi cells (marked with GFP) contain smaller dLAMP-3xmCherry dots than the neighboring control cells. (F,G) mCherry-GFP-Atg8a with (G) or without (F) Rab39 RNAi was expressed in several cells in fat tissues of L3 stage starved larvae. Magenta alone depicts autolysosomes (marked by arrows), as GFP is quenched in acidic environment. Please note that the difference in nuclei size is the result of rapid nuclei size change due to development and it does not affect autophagic flux. (H) Rab39QL-YFP was expressed in cell clones, while 3xmCherry-Atg8a reporter was expressed throughout the fat body tissue of L3 stage starved larvae. By expressing the constitutively active form of Rab39 in an ectopic manner, large mCherry-positive vesicles appeared. (I) Colocalization experiment in L3 stage starved larvae of Rab39QL-YFP and LTR shows a marginal overlap between the two signals, suggesting an autolysosomal Rab39 localization. Boxed regions are enlarged in (F,G,I) and colocalizing signals are marked by arrows. Heterozygous Rab39C-R animals with (F) or without (C) the indicated transgenes were used as controls.