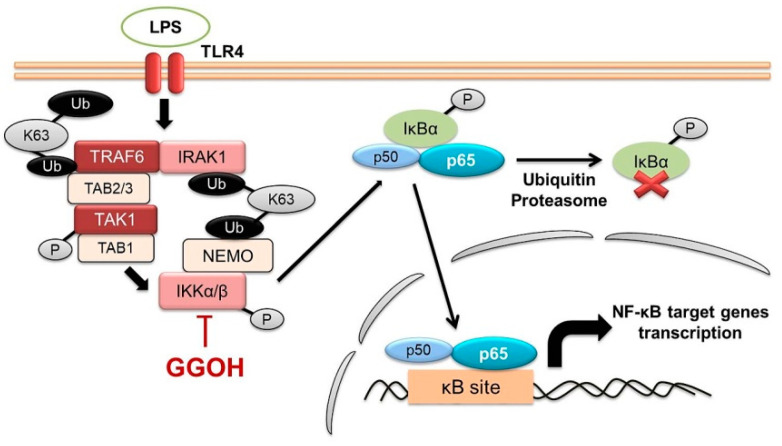
Figure 8.
Possible molecular mechanism by which geranylgeraniol (GGOH) inhibited LPS-induced inflammation in MG6 cells. LPS induced NF-κB activation via the subsequent phosphorylation of TAK1, IKKα/β, p65, and IκBα, which triggered IκBα degradation and p65 nuclear translocation. However, GGOH administration inhibited IKKα/β phosphorylation, which possibly modulate the downstream signaling cascade. Additionally, it also reduced TAK1 phosphorylation and attenuated upstream signaling events, especially IRAK1. Even though further investigation is necessary, there is a possibility that GGOH interferes with the interaction between IRAK1 and NEMO, thereby reducing IKK phosphorylation effectivity.