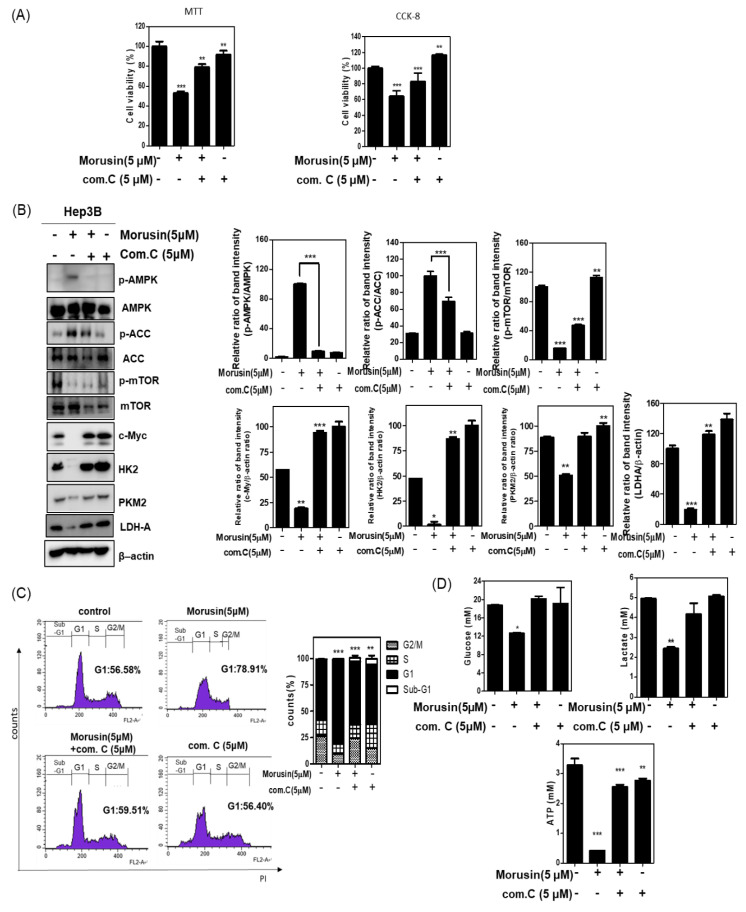
Figure 4.
Effect of compound C on glycolysis related proteins and G1 arrest in Morusin treated Hep3B cells. (A) Hep3B cells were treated with Moursin in the absence and presence of compound C. Cell viability was evaluated using MTT and CCK-8 assays. (B) Effect of AMPK inhibitor compound C on glycolysis related proteins in Morusin treated Hep3B cells. Hep3B cells were treated with Morusin (5 μM) in the presence or absence of compound C (5 μM) for 24 h. Cell extracts were prepared and subjected to Western blotting with the antibodies of p-mTOR, mTOR, p-ACC, ACC p-AMPK, AMPK, c-Myc, HK2, PKM2, and β-actin. Data represent means ± SD. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001 vs. untreated control. (C) Effect of compound C on G1 arrest in Morusin treated Hep3B cells. Hep3B cells exposed to Morusin (5 μM) in the presence or absence of compound C for 24 h were subjected to cell cycle analysis by staining with propidium iodide (50 μg/mL) (n = 3). (D) Glucose, lactate, and ATP in conditioned medium were measured by using colorimetric assay kit. Data represent means ± SD. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001 vs. untreated control (n = 3).