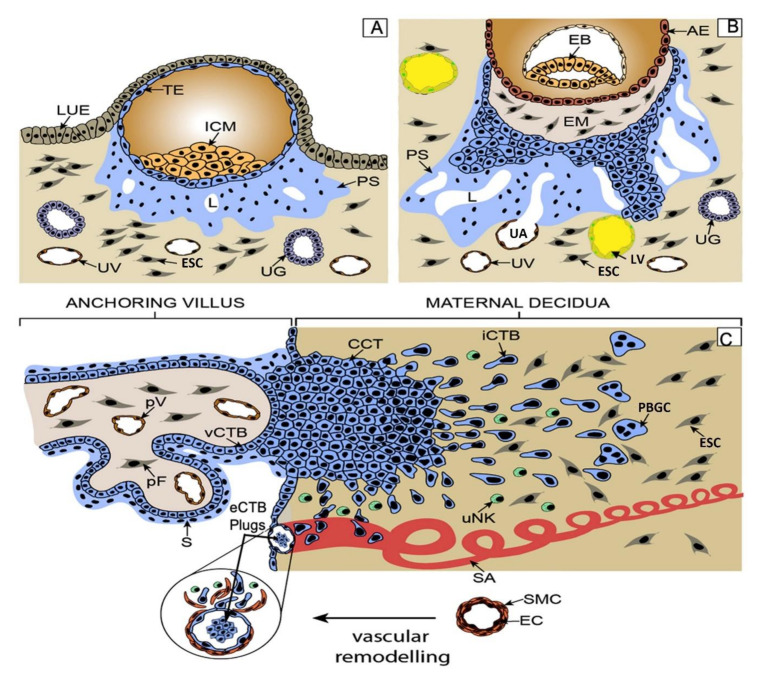
Figure 1.
Adapted from [6] with permission. (A) Shortly after implantation (end of first week), stem cells of the trophectoderm give rise to the primitive syncytium (PS) by cell fusion. Lacunae (L) develop in the PS, as the precursor of the intervillous space. Invasion of the PS into uterine glands allows “uterine milk” to fill up the lacunae (histotrophic nutrition). Later, with invasion of the PS into uterine vessels (UV/UA), maternal blood fills the lacunae (hemotrophic nutrition). Lymphatics (LL) are also invaded. (B) During the end of second week, proliferative cytotrophoblasts (CTBs) break through the PS, forming primary villi. (C) During the third week, tertiary villi are formed by migration of the extraembryonic mesoderm followed by vascularization. At distal sites, proliferative cell columns are formed which give rise to different invasive extravillous trophoblast (EVT) subtypes. Interstitial cytotrophoblasts (iCTBs) migrate into the decidual stroma and differentiate into placental bed giant cells (PBGCs). Endovascular trophoblasts migrate into spiral arteries and contribute to uterine natural killer (uNK) cell-initiated remodeling of spiral arteries (SA). Bulmer et al. (2020) [7] recently challenged the long-held view that endovascular trophoblasts (eCTBs) replace the endothelium of spiral arteries during arterial remodeling. By immunostaining a large number of chorionic villus biopsy samples, they found that, while sCTB plugs appear within the arterial lumen, arteries were found with either missing or intact endothelium, but never lined by eCTBs. AE, amniotic epithelium; CCT, cell column trophoblast; ESC, endometrial stromal cell; EB, embryoblast; EM, extraembryonic mesoderm; eCTB, endovascular cytotrophoblast; PBGC, placental bed giant cell; ICM, inner cell mass, iCTB, interstitial cytotrophoblast; LUE, luminal uterine epithelium; L, lacunae; LL lymphatic lumen; pF, placental fibroblast; PS, primitive syncytium; pV, placental vessel; SA, spiral artery; S, syncytium; TE, trophectoderm; UG, uterine gland; uNK, uterine NK cell; UV, uterine vein; UA, uterine artery; vCTB, villous cytotrophoblast.