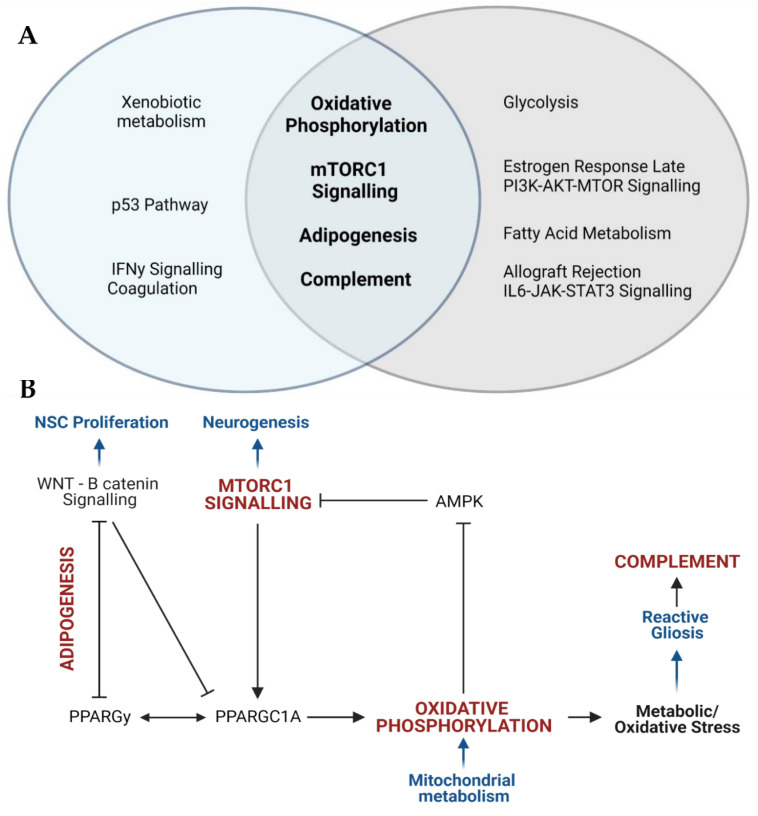
Figure 2.
ASD proteomic profiles converge on four canonical pathways involved in mitochondrial metabolism, neurogenesis and neuroinflammation. (A) The Venn diagram shows the Hallmark canonical pathways implicated in seven or more independent datasets (in blue), the enriched canonical pathways in the 121 differentially expressed proteins implicated in transcriptomic and DNAm datasets (light grey) and the pathways that overlap (in bold font). (B) The four pathways implicated in both analyses (Figure 2A) converge on the regulation of the following biological processes (in blue): neural stem cell proliferation, neurogenesis, mitochondrial metabolism, and inflammation. The mTORC1 signalling pathway induces oxidative phosphorylation via the activation of camp-responsive element binding protein 1 (CREB1) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PPARGC1A), which regulates mitochondrial metabolism and the antioxidant response. PPARGC1A is regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARGy), which acts as a master regulator of lipid metabolism and is essential to induce adipogenesis. Adipogenesis is negatively regulated by WNT signalling, which inhibits PPARGy, PPARGC1A and mTORC1 signalling to regulate stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Mitochondrial metabolism regulates metabolic and redox homeostasis which governs the inflammatory profile of microglia. Oxidative stress leads to the over proliferation of reactive microglia, which triggers the pro-inflammatory complement response.